
Snakes are carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes. These long and legless animals have a very unique anatomy that make us question how exactly their body works. This is especially true given that this group of animals have gone through a great variety of adaptations and physiological and anatomical modifications throughout its evolution.
One of the most common misconceptions of snakes is that they are deaf, however, that's not exactly the case. So, can snakes hear without ears? In this AnimalWised article we are going to explain snake hearing and their auditory anatomy.
Can snakes hear?
Contrary to popular belief, snakes are not deaf and can hear well. However, unlike other reptiles, snakes do not have an eardrum or tympanic cavity. They have also lost other hearing structure though out their evolution.
How do snakes hear?
Snakes hear through vibrations they perceive thanks to their jaw bones. Therefore, although they do not have a visible ear similar to ours, they can hear through vibrations. this way, they are able to determine the location thanks to the sound waves produced by movement. This occurs due to sound waves that are produced on these surfaces, which radiate around them very quickly, allowing snakes to hunt their prey without failing.
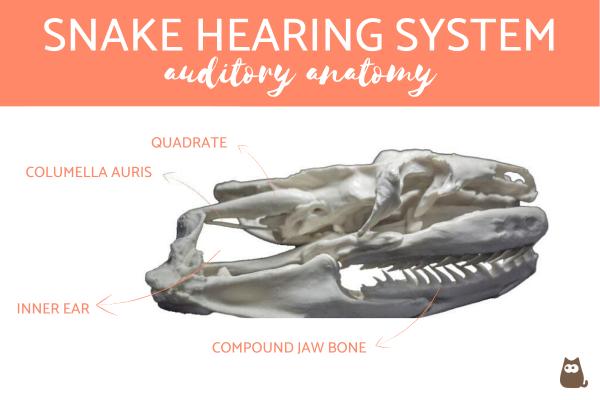
Snakes actually have formed an inner ear, with no eardrum, that is directly connected to their jaw bone (quadrate bone). This bone rests on the ground and slightly moves in response to vibrations while they slither on the ground. Snakes have a hearing range of 80-600 Hz, although some species can hear up to 1000 Hz. Given that the average human voice is around 250 Hz, snakes can actually hear us talk. Nevertheless, snakes can better perceive low-frequency sounds.
Snake hearing system
Now that we know that snakes can hear through the vibrations of sound waves, it's time to get to know their hearing system as it's very different to ours. First things first, snakes have lost various hearing structures and currently do not have external ear or even an eardrum. Nevertheless, they do have an inner ear that consists of:
- Hair cells
- Auditory nerve fibers
- Basilar membrane
- Cochlear duct
- Semicircular canals
- Sacculus
This inner ear structure is directly connected to their jawbone, in other words, the mandible. This consists of:
- Compound jawbone
- Columella auris
- Quadrate
- Supratemporal
These two structures work together to percieve movement through sound waves. As we've previously mentioned, snakes can impressively perceive low-frequency sounds.
Somatic hearing
Now that you know that snakes are not deaf, how they perceive sound, and how their auditory systems work, keep learning more about these fascinating animals with our article about if snakes have bones.
If you want to learn more about snake hearing, we invite you to also watch this YouTube video from Wicked Wildlife about a snake's auditory system!

If you want to read similar articles to Can Snakes Hear?, we recommend you visit our Facts about the animal kingdom category.
- Christensen, CB, Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., Brandt, C., & Madsen, PT (2012). Hearing with an atympanic ear: good vibration and poor sound-pressure detection in the royal python, Python regius . Journal of Experimental Biology, 215 (2), 331-342.
- Lillywhite, HB (2014). How snakes work: structure, function and behavior of the world's snakes . Oxford University Press.
- Scanferla, CA, Fernández, M., & Novas, FE (2010). The origin and early evolution of snakes: anatomical and phylogenetic analysis of the Cretaceous and Paleogenic ophidians of Patagonia and Bolivia .
- Young, BA (2003). Snake bioacoustics: toward a richer understanding of the behavioral ecology of snakes . The Quarterly Review of Biology, 78 (3), 303-325.