There are many important reason to neuter your dog. For the larger animal community, sterilizing dogs lessens the problems caused by overpopulation. For the individual, sterilizing can help the dog avoid various behavioral and health problems caused by the reproductive organs. These can range from avoiding aggression in some dogs to preventing the possibility of contracting various types of cancer in dogs.
However, do these health benefits significantly affect canine life expectancy? If we find out the life expectancy of fixed dogs, we can know do neutered dogs live longer? AnimalWised reveals that, although researchers have long thought sterilization might extend a dog's life, it is only relatively recently that science can confirm neutered dogs do indeed live longer.
Neutering in dogs
Dog neutering is often confused with sterilization. Although there are similarities, it is important to distinguish between the two. Sterilization refers to making the dog sterile, i.e. they cannot reproduce. However, this can be temporary. For example, if the dog is chemically sterilized, once they stop taking fertilization preventing drugs, they will once again be able to mate.
Neutering in dogs refers to the process of permanently sterilizing the dog. This means they will no longer be able to reproduce at all. This is done in two major ways, depending on the sex of the dog:
- Neutering male dogs: the process of castration means the male dog's testicles are removed completely. This not only prevents the dog from producing sperm, but it also stops male hormone production. The result is that the dog will reduce hormone related behaviors such as pursuing a female mate, aggression and potential escape.
- Neutering female dogs: for females, there is the option of removing the dog's ovaries or both their ovaries and the uterus. Both are known as spaying, but spaying is most often referenced to a full ovariohysterectomy (removing both ovaries and uterus).The latter is more common as it not only prevents reproduction, but it stops the dog from having uterine diseases such as cancer or canine pyometra. Removing the ovaries also prevents the dog from producing certain hormones to the extent they would before and stops them from entering the estrus cycle, know in dogs as the heat period. The signs of when a dog is in heat will let you know whether or not they are neutered.
The difference between sterilization and neutering in dogs is important as the former does not affect life expectancy in the same way. Hormonal imbalance and diseases of the reproductive organs are much lesser when full neutering has taken place.
While the neutering procedure is relatively very safe, we still need to observe for any complications. Take a look at our article what to do if your female dog bleeds after spaying to know more.
How long do neutered dogs live?
First of all, it is very important to note that there are many factors which will affect a dog's life expectancy, regardless of whether they have been neutered. Even their breed will have a determining factor, but so too will their care, the use of preventive medicine and their fortune. However, we can generalize about how long fixed dogs will live compared to non-neutered canines.
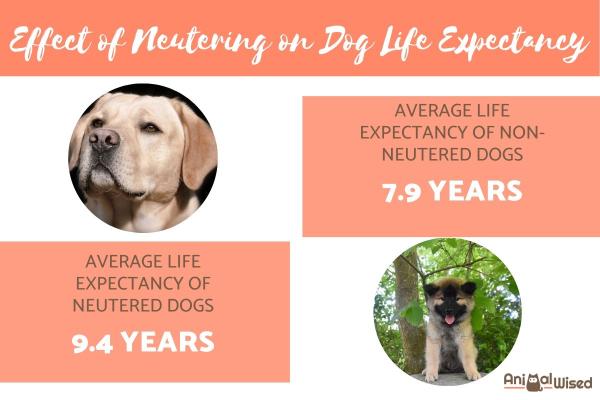
Scientists at the University of Georgia studied the records of 40,139 dog deaths between the years 1984 and 2004. By collating all of the data, they discovered that the average life expectancy for unneutered dogs was 7.9 years. The life expectancy of neutered dogs was 9.4 years. This goes to prove that there is almost 2 years difference in life expectancy between dogs that a neutered and those that are not.
At the time the research was carried out, it was already known that organisms which do not produce generally have a longer life span than those which do. The reasons why have so far alluded a concrete conclusion, although there are theories on the matter.
In the case of dogs, this study revealed some interesting correlations. It was found that neutered dogs were more likely to die from cancer or autoimmune disease. Those which are not were more likely to die from either infectious diseases or trauma. This may, in part, explain the difference in life expectancy between the two groups.
Scientists indicate that the mortality age of the cases studied were lower than in the general dog population, due to the fact they were reports based on animals admitted to veterinary clinics due to sickness. However, they were still able to extrapolate potential life expectancies for neutered and non-neutered dogs regardless.

Why do neutered dogs live longer?
The answer to this question is still not fully known, despite the results of the study. What we do know is that the presence of certain hormones which have been removed due to the neutering procedure, lessens the risk of certain problems. These hormones, including progesterone and testosterone could suppress the immune system, explain the greater risks of infection.
Another reason is behavioral. Since male dogs will try to find a female in heat, they will often leave the security of their home to find them. The sexual drive is so strong, they can even become lost, have an accident or even be collected as an abandoned dog. Neutered dogs will be more likely to stay at home and have little interest in running away.
While neutering does provide certain benefits, it is also important to note it is not a miracle protection against any canine health problem. We still need to provide them with the correct nutrition, stimulate their cognition, avoid stress and provide preventive care in the form of vaccinations, deworming and veterinary checkups. Ensuring their general well-being is a multi-faceted process.

At what age should you neuter your dog?
The ideal time to neuter a dog depends on their age, sex and size. For smaller female dogs, it is best to spay them before they enter their first heat cycle. For larger dogs, it is better to wait until they have fully physically developed. For male dogs, it is ideal to castrate them between the ages of 5 and 6 months. Senior dogs, usually those over the age of 7 years should not be neutered at all.
The procedures for sterilizing and neutering dogs can be broken down as this:
- Ligation (sterilize): in this case two ligatures are made surgically (uterus of females or on the spermatic cord of males) and a cut is made in the middle. In this case the animal continues to generate hormones, although it cannot reproduce.
- Ovariesctomy (neuter): the gonads (ovaries or testicles) are removed. In males this is known as castration.
- Hysterectomy (neuter): the uterus is removed.
- Ovariohysterectomy (neuter): the uterus and ovaries are removed.
If you are considering neutering a dog to increase its life expectancy, you will need to discuss the procedure with your veterinarian. Ideally it will be carried out when they are young, but this is not always possible. The veterinarian will determine the best course of action considering the well-being of the individual dog.
When male and female dogs are not neutered, they can copulate. When this happens, it can look as if they get stuck, something we explain in this video below:

If you want to read similar articles to Do Neutered Dogs Live Longer?, we recommend you visit our Facts about the animal kingdom category.
- Hoffman, J. M, Creevy, K. E., & Promislow, D. E. L. (2013). Reproductive Capability Is Associated with Lifespan and Cause of Death in Companion Dogs. PLoS ONE, 8(4): e61082
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061082