
Rabbits are small mammals that are now a common domestic pet. We are oftentimes surprised and entertained by our pet's behaviour. We try to understand their behaviour and experience so as to provide them with a good quality of life.
A common question rabbit companions have is, what do rabbits see? What's the difference between human and rabbit vision? In this AnimalWised article we are going to explain a rabbit's vision and the differences with ours. We also provide photos so you can understand who your rabbit perceives you and their environment.
Do rabbits have good vision?
In the wild, rabbits are prey animals. This means that they are often sought out and captured by predators to be eaten as food. While predator animals have a great depth of field to help them catch their prey (straight ahead), prey animals have a larger field of view (sideways) to help them escape predators.
Although, in comparison to humans, rabbits don't have the best eyesight to look at things up close, they do have a great field of view that works best for their function in the wild. Prey animals don't need a binocular vision as much as they need a wide field of view. This is because they are usually attacked from all sorts of angles and need to be able to detect the danger quickly in order to escape and survive.
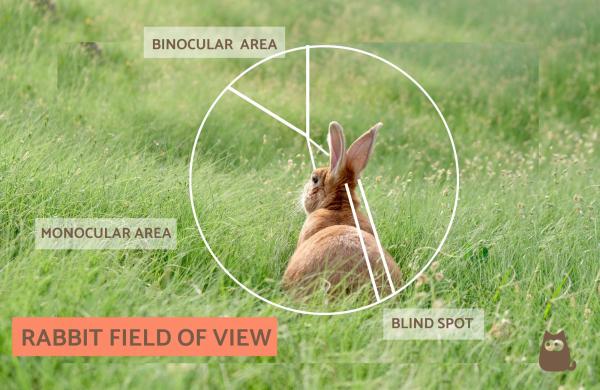
A rabbit's field of view
In difference to humans and other animals, rabbits have their eyes on the sides of their face, giving them lateral vision and a great field of view. Thanks to this lateral vision, rabbits have a nearly full 360º vision. Their great vision helps them stay alert and escape predators if needed.
Monocular
Monocular vision is the vision in which eye eye is used separately. A rabbit's monocular vision is located on the sides of their field of view. These two wide angles of view allow them to see in 2D. By using monocular vision their field of view is wider, their depth of field is limited. Nevertheless, for a wild rabbit, depth of field may not be as important to detect nearby predators.
Binocular
Binocular vision is the vision in which both eyes are used at the same time. This helps the depth of field, allowing rabbits to see things in 3D. Rabbits of a narrow binocular vision, as you can see in the photo below.
Blind spot
The small price rabbits have to pay for this remarkable field of view is their small blind spots located right in front of their eyes and behind their ears. This is why if you're standing directly in front of them, they may not perceive you at first. Nevertheless, their great hearing skills make up for these blind spots and help them be very observant of their environment. We must also remember that domestic rabbits have gotten used to being in a safe home and so, will not be as alert as wild rabbits need to be in order to survive.
Can rabbits see color?
Yes, rabbits can see colors but they don't see the same colors as humans. Rabbits have dichromatic color vision, meaning that they have two types of functioning color receptors, called cone cells, in their eyes. While humans can observe a combination of red, blue and green, rabbits can only observe two colors: blue and green. Meaning that, rabbits are somewhat color blind by human standards.
So, why can't rabbits perceive other colors? Let's analyse their color vision:
- Cones: detect color under well-lit conditions (photopic vision). Rabbits have about 18,000 per sq. mm at peak density. About 10x less than humans. In other words, rabbits are slightly colorblind by human standards.
- Rods: detect less detail & no color, but they are much more sensitive to light (scotopic vision). Rabbits have about 300,000 per sq. mm. at peak density. About 2x the amount of humans. This means that rabbits can see much better in the dark.
In other words, rabbits do have cone photoreceptors – but only the green and blue cones (520nm and 425nm).This means that, compared to most humans, they are slightly colour-blind (protanopic or dichromatic). An interesting fact is that some humans actually have the same color-blindness that rabbits have. So, in conclusion, rabbits do see colours, but will find it difficult differentiating reds and greens, and also blues and greens.
Therefore, although rabbits don't always see the same colors as humans, they can see the same color-wavelength combinations and tell many of them apart.

Can rabbits see in the dark?
As we've previously mentioned, rabbits have about 2x rods as humans. This helps them see in the dark much better than we can. However, rabbits are not nocturnal animals. In fact, they see best at dawn or dusk as they are crepuscular animals. This is how the combination of the amount of rods they have, plus their blue and green cones, help them detect any nearby predators.
Rabbits are also known for being sensitive to direct sunlight because of their restricted contraction of their pupils. The human eye has an area called centralis that is slightly indented and although rabbits also have a centralis, it is not indented. This results in rabbits having a somewhat grainy vision in the light. In fact, rabbits are 8x more sensitive to direct light than humans.

Difference between human and rabbit vision
We've gone through the different aspects of a rabbit's vision, mentioning its difference to the human eye. Here is a summary of the differences between the human eye and a rabbit's vision:
- Field of view: rabbits have a much larger field of view than humans as their eyes are located at the sides of their face.
- Depth of view: humans have a larger depth of view thanks to our binocular vision, allowing us to mostly see in 3D, whereas rabbits have a more narrow binocular vision and mostly use their monocular vision to watch out for predators.
- Cones: rabbits have about 10x less cones than humans. Making them colorblind by human standards.
- Colors: rabbits mostly see blues and greens, whereas humans can mostly see red, blue and green.
- Rods: rabbits have about 2x the amount of rods that humans have. Allowing them to see much better at dusk or dawn.
- Sensitivity to light: rabbits are 8x more sensitive to light than humans.
- Grainy vision: rabbits have a more grainy vision than humans.
Fun facts about rabbit vision
- Rabbits are born with closed eyelids
- They open their eyelids when they're about 10 days old
- Rabbits have a third eyelid
- Rabbits blink once every (approximately) 5 minutes
If you want to read similar articles to Rabbit Vision vs. Human Vision, we recommend you visit our Facts about the animal kingdom category.
- Gibb, JA (1990). The European rabbit Oryctolagus cuniculus. JA Chapman and JEC Flux (a cura di), Rabbits, Hares and Pikas-Staus Survey and Conservation Action Plan. IUCN / SSC Lagomorph Specialist Group, 116-120.
- Hughes, A. (1971). Topographical relationships between the anatomy and physiology of the rabbit visual system . Documenta Ophthalmologica, 30 (1), 33-159.
- Yokoyama, S. (2002). Molecular evolution of color vision in vertebrates. Gene, 300 (1-2), 69-78.