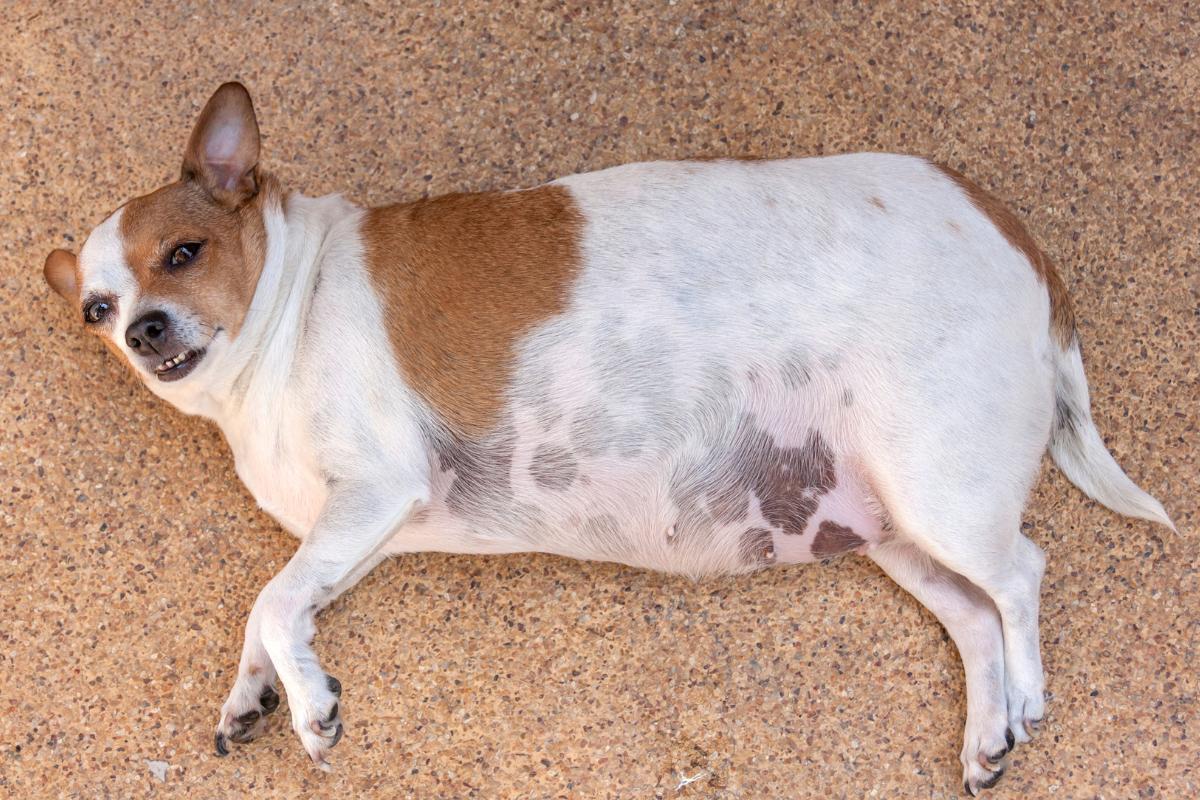
Distended Abdomen in Dogs

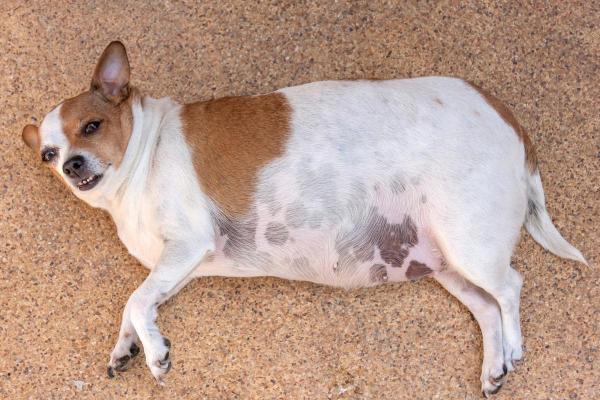

See files for Dogs
Abdominal distension, commonly known as a swollen belly, is a frequent veterinary complaint among dogs. It manifests as an abnormal enlargement of the abdomen, often accompanied by signs of discomfort or pain. While a mildly distended abdomen can sometimes be attributed to harmless factors like a hearty meal, it can also indicate underlying medical conditions that require prompt attention. Delaying veterinary attention can lead to complications and worsen the dog's condition.
The following AnimalWised article explain what abdominal distension in dogs is, its most common symptoms, and treatment options.
What is abdominal distension in dogs?
Abdominal distension refers to the enlargement and altered shape of the abdomen, making it rounder and more prominent. This expansion can result from an abnormal increase in fluid, gas, or organ size within the abdominal cavity. Dogs displaying abdominal distension may be dealing with various health issues, underscoring the importance of promptly consulting a veterinarian to identify the root cause and address the problem.
It's crucial to distinguish abdominal distension from obesity, where weight gain occurs gradually, and excess fat can be felt in front of the abdominal wall upon palpation. With abdominal distension, the abdomen contracts when pressed, and the feel can vary based on the underlying cause, ranging from hardness to a sense of fullness with gas. Recognizing these differences is key in determining if a dog is experiencing bloating.
Symptoms of abdominal distension in dogs
Abdominal distension in dogs manifests as a sudden and conspicuous alteration in the size and shape of the abdomen. Associated symptoms may include:
- Weight gain
- Lethargy
- Weakness
- Exercise intolerance
- Increased respiratory rate
- Difficulty breathing
- Reduced appetite
- Arcades
It's important to note that these symptoms can be indicative of various underlying health issues, and not all dogs with abdominal distension will exhibit the same set of symptoms.

Causes of abdominal distension in dogs
Abdominal distension, also known as a swollen belly, can be caused by various factors in dogs. Understanding these root causes involves examining specific aspects:
Increased organ size
When the abdomen feels firm and irregular upon touch, it may indicate enlarged internal organs. Further testing is needed to identify the affected organs. This enlargement is often linked to conditions like tumors, torsion, or congestion of the organs.
Fluid accumulation
Palpating the abdomen in this case feels similar to pressing a water balloon, with even movement and minimal resistance. This fluid buildup can be associated with conditions like effusions, where different fluid types increase. It may be linked to heart problems, abdominal inflammation, bladder rupture, abscesses, pyometra, urinary obstructions, or digestive obstructions.
Gastrointestinal content
In cases involving the accumulation of digestive contents, palpation yields a more varied feel due to the diverse nature of these contents. Causes may include constipation, megacolon, paralytic ileus, binge eating, or an abundance of intestinal parasites.
Gas
When the abdomen feels like squeezing a balloon, accompanied by audible intestinal noises (borborygmus), it indicates the presence of gas. Causes range from gastric dilation-torsion and intestinal torsion to gastrointestinal tract rupture, post-surgery effects, emphysematous bacterial infections, or penetrating trauma.
Abdominal atony
Abdominal atony refers to a condition where the abdominal muscles lose their ability to contract, resulting in a completely relaxed abdomen. This condition is associated with hormonal diseases such as hypoadrenocorticism.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is an obvious cause to consider, particularly in intact female dogs. Interested in the journey of canine motherhood? Take a closer look at the transformative stages of dog pregnancy in this other article.
Due to the diverse potential causes, a thorough veterinary examination is crucial for accurately diagnosing the specific underlying issue contributing to abdominal distension in each case.
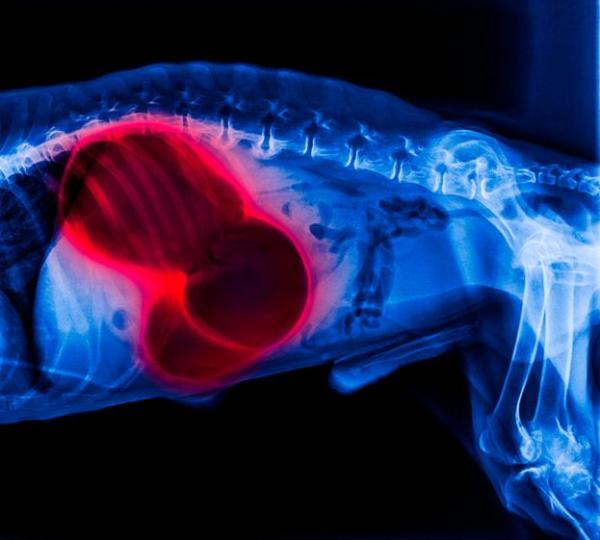
Diagnosis of abdominal distension in dogs
Diagnosing the cause of abdominal distension in dogs is a critical and time-sensitive process, often linked to emergencies.
Seeking veterinary attention promptly is crucial, as a few hours can make a significant difference in the dog's survival. Key diagnostic tests include:
- Patient examination: a general examination assesses the dog's overall condition, especially if signs of shock are present. Immediate symptomatic treatment may be necessary.
- In-depth examination and clinical history: gathering detailed information about the dog helps quickly eliminate potential reproductive, digestive, or other system-related pathologies.
- Blood and serum analysis: these tests provide insights into the patient's current condition, the severity of the situation, and the functional status of organs under stress.
- Urinalysis: helps understand the origin of the disease or rule out urinary pathologies compared to other diagnostic tests.
- Diagnostic imaging: X-rays and abdominal/thoracic ultrasound play a crucial role in ruling out pathologies affecting organs such as the heart, liver, spleen, or bladder.
- Abdominal puncture: if the origin remains elusive after previous tests, abdominal puncture can identify the type of fluid in the abdomen and its origin.
- Laparotomy: in borderline situations where organ rupture is suspected, an exploratory laparotomy helps locate and address the problem.
- Biopsy: in specific cases, a biopsy is necessary for an in-depth examination of tissue to rule out pathologies like cancer.
Given the urgency of the situation, a comprehensive approach involving these diagnostic tests is crucial for a timely and accurate understanding of the underlying cause of abdominal distension in dogs.
Interested in the insights revealed by dog blood tests? Explore the basics of this essential diagnostic tool in our comprehensive guide.
Treatment of abdominal distension in dogs
The treatment for abdominal distension in dogs depends on the underlying cause, so it's crucial for a veterinarian to conduct a thorough examination and diagnostic tests to identify the specific problem. However, here are some general considerations for treatment:
- Emergency care: if the dog shows signs of distress or shock, immediate stabilization and symptomatic treatment may be necessary. This may involve intravenous fluids, oxygen therapy, or pain medication.
- Diagnostic evaluation: comprehensive diagnostic tests, including bloodwork, urinalysis, and imaging studies (X-rays, ultrasound), help pinpoint the cause of abdominal distension. This information is essential for developing an effective treatment plan.
- Medical management: treatment may involve medications to address specific conditions, such as endocrine or cardiac diseases. Diuretics may be administered in cases of fluid accumulation to promote fluid removal.
- Surgery: in certain situations, surgical intervention may be required to address issues like organ torsion, tumors, or ruptures. High-risk surgeries should be carefully considered, taking into account the overall health of the dog.
- Fluid drainage: if there is an accumulation of fluids in the abdomen, drainage through procedures like abdominal puncture may be necessary. This can help relieve pressure and discomfort, and it may also help to prevent further complications.
- Monitoring and supportive care: continuous monitoring of the dog's vital signs and response to treatment is essential. This allows the veterinarian to assess the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments as needed. Supportive care, including intravenous fluids and pain management, may be provided as needed to help the dog recover.
- Nutritional support: dogs with abdominal distension may experience a loss of appetite. Nutritional support, such as syringe feeding or specialized diets, may be recommended to help the dog maintain its strength and promote healing.
- Postoperative care: after surgery, postoperative care is crucial. This includes monitoring for complications, providing pain medication, and ensuring proper healing.
It's important to remember that the specific treatment plan will vary based on the diagnosis. Pet owners should work closely with their veterinarian to understand the recommended course of action and follow through with prescribed treatments for the best possible outcome.

Are there home remedies for abdominal distension in dogs?
Abdominal distension in dogs is a serious condition that often requires prompt veterinary attention due to the potentially life-threatening underlying causes. While there may be home care measures to alleviate mild gastrointestinal discomfort in dogs, it's crucial to recognize that these are not substitutes for professional veterinary evaluation and treatment.
If you suspect abdominal distension in your dog, it is strongly recommended to consult with a veterinarian. Home remedies alone are not sufficient for addressing the diverse and serious conditions that can lead to abdominal distension.
This article is purely informative. AnimalWised does not have the authority to prescribe any veterinary treatment or create a diagnosis. We invite you to take your pet to the veterinarian if they are suffering from any condition or pain.
If you want to read similar articles to Distended Abdomen in Dogs, we recommend you visit our Intestinal problems category.
- Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine , 8th Edition.