How Long Does a Wasp Live?

The lifespan of wasps varies according to their species and the type of wasp within a hive. Grouped within the order Hymenoptera, wasps are seen as being more aggressive than other members of this order such as bees. Most wasps do not make honey and are considered more aggressive than bees. This does not mean they are not incredibly important in their ecosystem. They pollinate plants and control the populations of other insects which helps to maintain ecological balance.
At AnimalWised, we discover the lifespan of wasps by asking how long does a wasp live?
How long do wasps live?
As stated in the introduction, the species of wasp will have a bearing on their lifespan. So too does their sex. Females will live longer than male wasps within the same colony. How long a female wasp will live depends on their role within the hive and their species. For example, queens, solitary wasps and workers will have different life expectancies:
- Queen: the wasp with the longest lifespan is the queen. She will live for a about a year.
- Workers: also female wasps, these types of wasp only live between 12-24 days.
- Male wasps: the main purpose of male wasps is to fertilize the queen during mating season. They do not usually outlast this time, meaning they live from a few days to a few weeks.
The species also causes some variance in how long does a wasp live. We will look at the lifespan of different types of wasp species below:
- Dusky paper wasp (Polistes fuscatus): it is native to North America. Queens live for about a year, the total time in which they develop and found a colony. Males live for a few months while breeding.
- Oriental hornet (Vespa orientalis): this species is native to Africa, Asia, and part of Europe. Queens live for about a year. The workers live less than the queens. Males live for a few months because they are inactive in winter, along with the rest of the colony. Once the queens are fertilized in the fall, they die.
- Asian giant hornet (Vespa mandarinia): it is the largest species of wasp and is native to Asia. As with the previous wasp species, the queens live one year. Worker wasps have a lifespan from spring to winter. For their part, the males die after mating in the fall.
- Eastern yellowjacket (Vespula maculifrons): this species is native to North America. The queen lives one year. The workers live from summer to winter. The males die when breeding in the fall, so that as adults they live for a few months, since they are born in the spring.
Learn about the difference between wasps, hornets and bees in our related article.
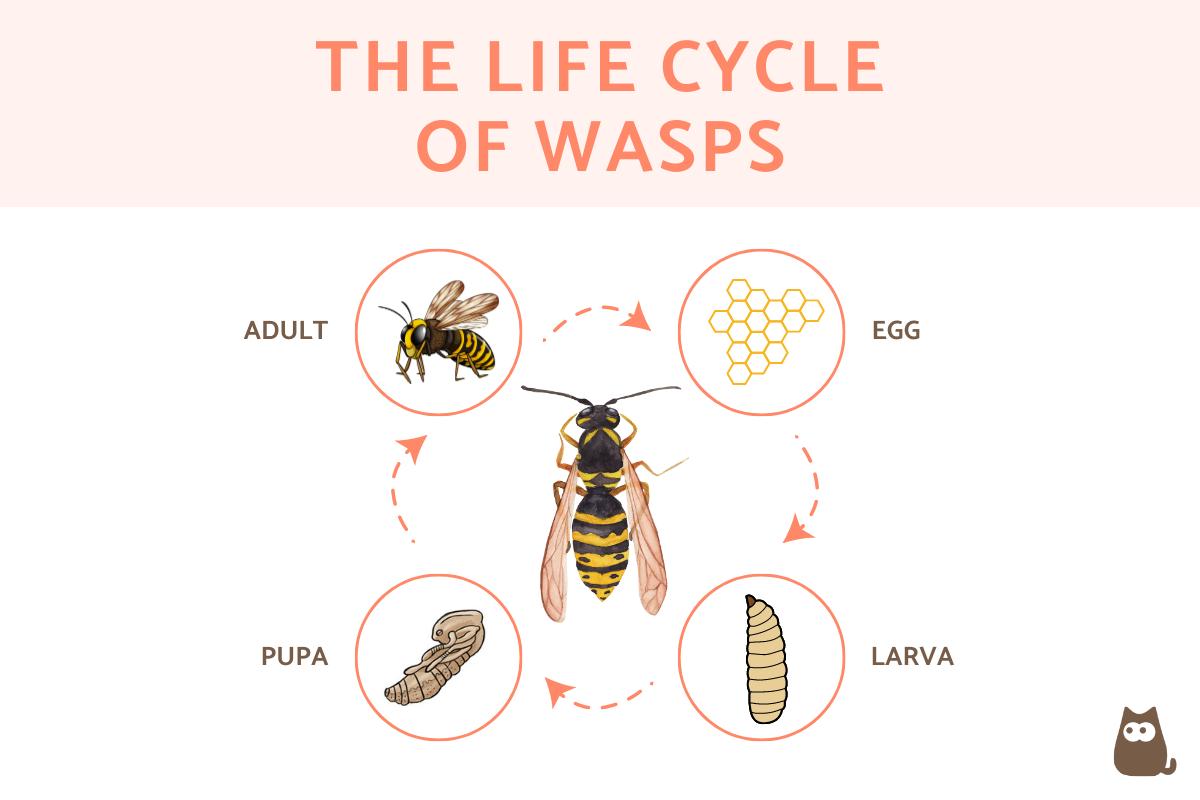
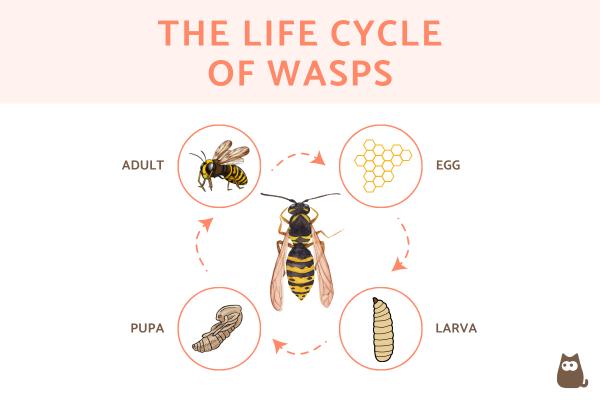
Wasp life cycle
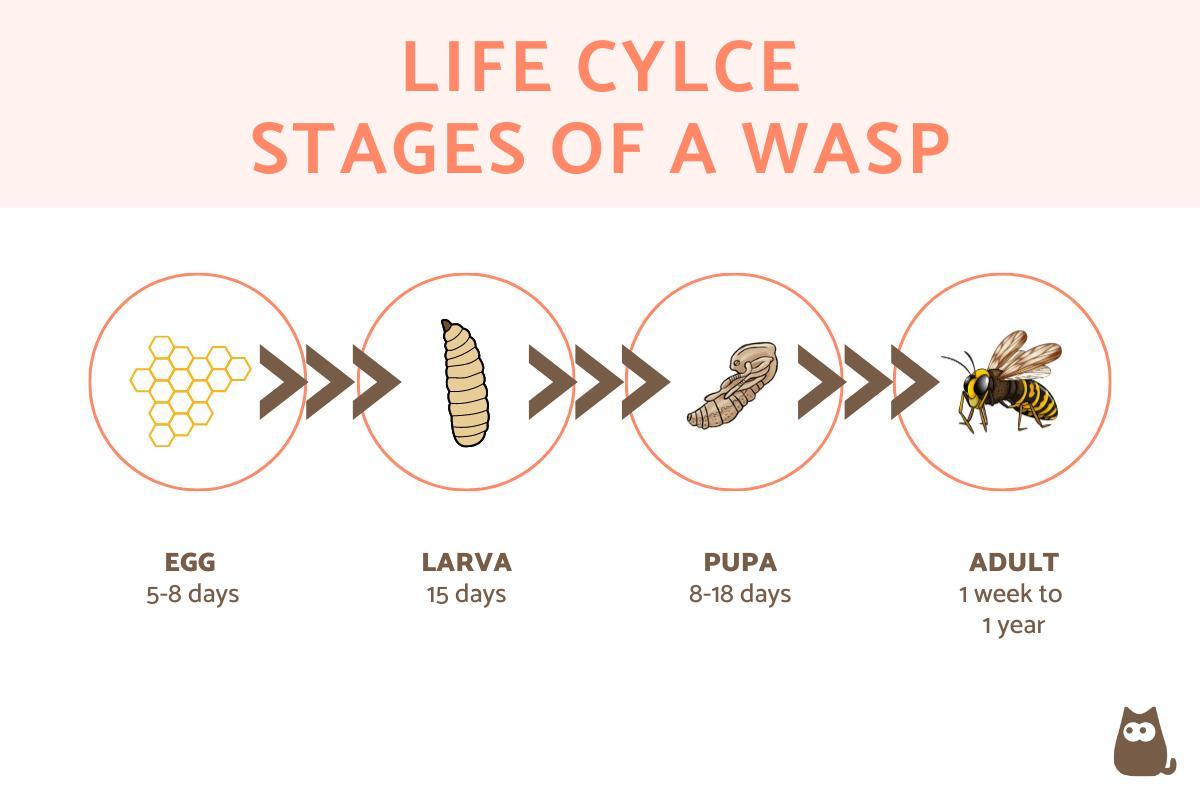
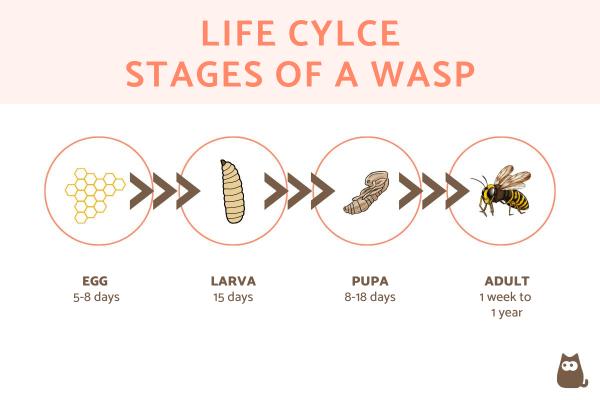
In general, wasps have a life cycle made up of egg, larva, pupa and adult phases. There may be particularities depending on the species and the environmental conditions, but in general the timeline of the life cycle of wasps is more or less the following:
- Egg: after being laid, the eggs take 5-8 days to hatch into larvae.
- Larva: the larvae go through several molts, which lasts around 15 days.
- Pupa: the pupal phase is a phase where there is no mobility, but there is activity. This lasts between 8 and 18 days approximately.
- Adult: this is the last stage of the life cycle of a wasp. As we have seen previously, it varies between queen, worker and males. Thus, the queen wasps live up to a year in this phase, the workers about a month and the males just a few weeks or months until they reproduce.
Apart from the above, wasps are usually divided into two groups:
- Social wasps: those that live in colonies.
- Solitary wasps: those that have solitary lives. These are the most common type of wasp.
Although in both cases they go through the same stages of egg, larva, pupa and adult, the life cycle is not exactly the same.
Social wasp life cycle
Social wasps have a caste system made up of queens, workers, and drones (males). Only the queens and males have any reproductive function, while the workers participate in expanding the nest and caring for the new generations.
The cycle of this group begins when a queen is fertilized. In areas with cold winters, the females remain inactive until the end of this season, becoming active again in spring. Once fertilized by the males, queens build a nest and lay the first eggs. This nest will only be worker wasps, which will be cared for by the queen.
After going through metamorphosis from the egg to the adult state, these workers begin to enlarge the nest. While there are different types of wasp nests, they are processed plant material. They house the new generations of wasp, which will also be many more individuals.
The next eggs to be laid by the queen may be fertile females, so that they will become future queens and found their own colony, as well as males that will also be fertile. The workers who are already fully developed as adults will participate in the care of these new generations.
Solitary wasp life cycle
As for solitary wasps, they also go through the egg, larva, pupa and adult phases. Since they do not live as adults in community nests, there is no caste system. Instead, an independent living female is fertilized by a male and lays her eggs. She then cares for them until they reach adulthood and separate to also lead a solitary life, either as males or females.
Take a look at our related article to discover whether wasps bite or sting.
How long do wasps live without eating?
Adult wasps usually feed on the nectar of flowers, fruits, sometimes dead animals and exudates from their larvae. In the larval phase, the wasps are carnivorous, so the adults capture other insects to serve as food for the developing wasps. Some adult wasps will eat when they predate on other animals, but it is not common.
Although wasps in the larval stage can be voracious, in the next phase of their development they do not feed. This means wasps in the pupal stage do not eat anything. This is because it is a stage of activity which is focused on metamorphosis continuing to pass into the adult phase. They stop moving and eating during this time. In this way, they can go without eating for around 8 to 18 days, depending on how long the pupal phase lasts.
Adult wasps that live in areas where there are winter seasons with significant temperature drops, usually take refuge. This can be in tunnels, on the ground or in logs where they remain inactive throughout this season. They will also stop feeding until they emerge in the spring when the temperatures are more hospitable. For all these reasons, wasps can live without eating for up to months at a time.
You can find out more about how other members of the Hymenoptera order eat with our article on what is the honey bee diet?
Factors that threaten the life expectancy of wasps
There are some natural factors that threaten the life expectancy of wasps. These include predation by other animals such as birds or small mammals. The weather can also affect them when adverse conditions occur, although wasps usually adjust their life cycle to protect themselves. An unusual climactic change can catch them by surprise.
The most devastating factors that threaten the life expectancy of wasps are those of human origin. These include the indiscriminate use of insecticides and other chemicals both in agriculture and in residential areas. Such insecticides are lethal to wasps. Deforestation in natural areas where wasps nest and vegetation fires also destroy hectares of forests, savannahs and other ecosystems typical of these insects.
Now that you know how long wasps live and what their life cycle is like, discover their importance to their ecosystems in the video below:

If you want to read similar articles to How Long Does a Wasp Live?, we recommend you visit our Facts about the animal kingdom category.
- Animal Diversity Web. (2020). Retrieved from: https://animaldiversity.org
- Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia. Wasp . Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved from: https://www.britannica.com/animal/wasp
- Fernandez, S., & Pujade-Villar, J. (2015). Order Hymenoptera. Retrieved from: http://sea-entomologia.org/IDE@/revista_59.pdf