Grasshopper vs. Cricket Differences

The difference between a grasshopper and a cricket can be difficult to determine. While the reasons are largely due to their close similarities in appearance and behavior, it is exacerbated by the fact there are some cricket species are known commonly or colloquially as grasshoppers. Both types of insect are found in the order Orthoptera, meaning they are types of arthropods. Taxonomically, we are aided by the fact that crickets can be found in the suborder Ensifera and grasshoppers are of the suborder Caelifera. There are other insect types in both these orders, but grasshoppers and crickets are separated from each other by them.
Entomologists will know the taxonomic rankings of these insects, but the rest of use can look at their characteristics and behaviors to know the grasshopper vs. cricket differences. AnimalWised helps you do so by providing 14 ways to tell them apart.
Are grasshoppers and crickets the same thing?
Although very similar in appearance and behavior, it is important to know that grasshoppers and crickets are different types of insects. Within each type of insect is further diversity, but there are certain characteristics common to one which is different in the other. Before we look at these differences, we can better understand the comparison between grasshopper vs. cricket by looking at their similarities.
Similarities between grasshoppers and crickets
The following are some of the similarities between grasshoppers and crickets:
- Straight wings: the name of the order Orthoptera alludes to this common trait of the group.
- Size: in general, they have medium to large sizes, although there are differences between species.
- Body: their bodies are both divided into the segments known as the head, thorax and abdomen.
- Head: their heads commonly form a right angle to the body.
- Mouth: the mouth is directed downwards.
- Jaws: both have oral apparatuses which allow them to chew vegetation.
- Eyes: the presence of compound eyes and ocelli are common to both crickets and grasshoppers.
- Antennae: they both have noticeable antennae emiting from their heads.
- Legs: both usually have a third pair of legs specialized for jumping.
- Wings: most have two pairs of wings, but they may be absent in certain species.
- Wing texture: the front wings are leathery and hardened, while the hind wings are membranous and larger.
- Folding wings: the second pair of wings fold into the first.
- Metamorphosis: both are animals that undergo complete metamorphosis.
- Sounds: it is common for them to produce stridulation, sounds produced from rubbing parts of the body.
Discover more about the specific behaviors of grasshoppers with our article on whether grasshoppers bite.

Physical differences between grasshopper and cricket
Now we know the common traits which mean people often confuse these insects with each other, we can help differentiate them with our comparison of grasshopper vs. cricket differences:
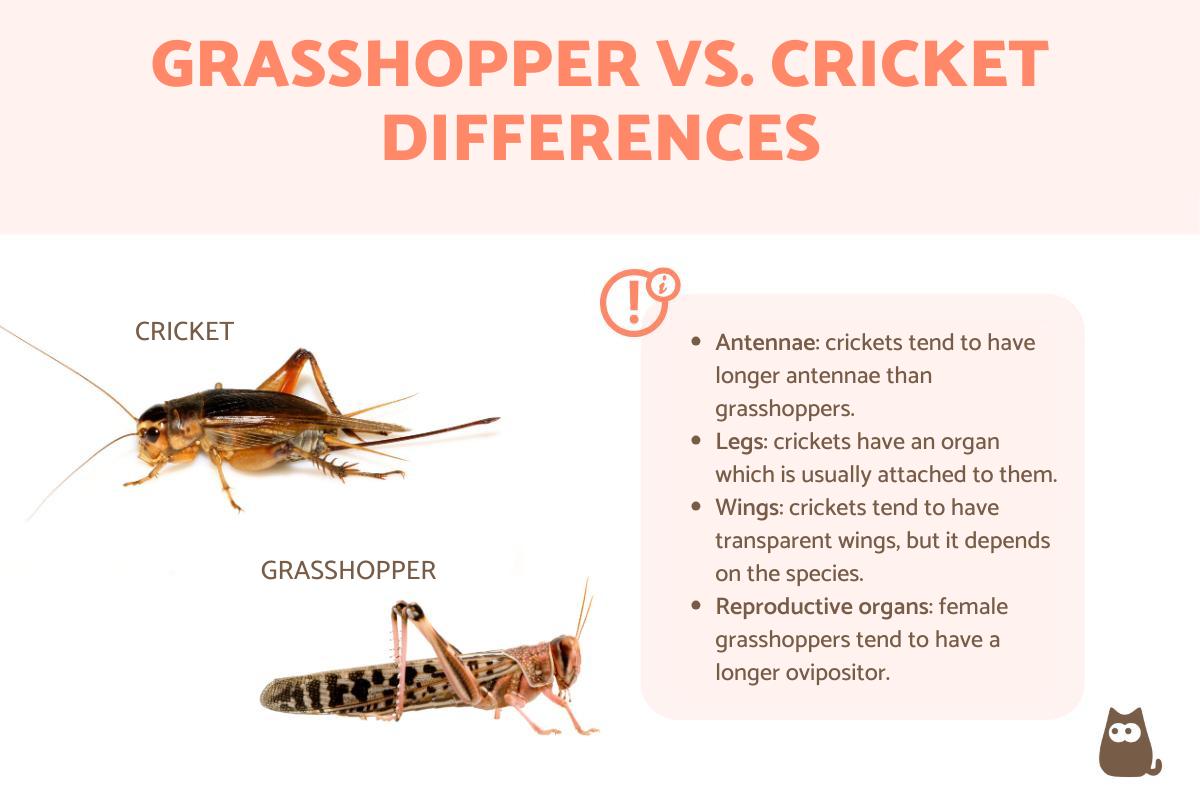
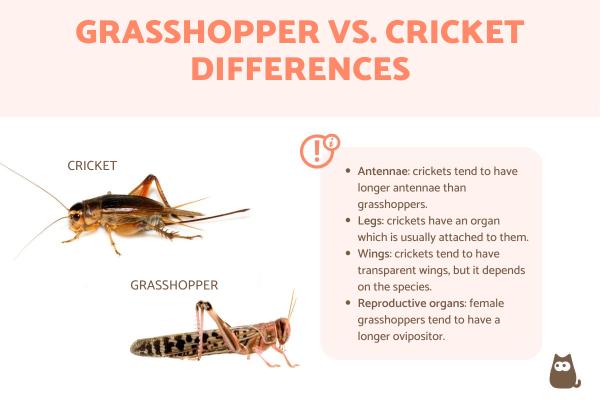
- Antennae: crickets have elongated antennae which can sometimes be as long as their body. They are filiform (i.e. threadlike) and have many rings or segments. Grasshoppers also have filiform antennae, but they tend to be shorter and can have other shapes. They are no longer than half their body and have few arteries which can easily be differentiated.
- Legs: the legs of both crickets and grasshoppers are made up of the coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia and tarsi. However, the number of each part depends on on the family. Crickets may have an organ used for hearing, which is relatively visible on the legs. In grasshoppers, the presence of this organ is located in the first segment of the abdomen. We can also find certain anatomical modifications in grasshoppers, which allow them to produce sounds by stridulation. Learn more with our article on how many legs do grasshoppers have?
- Wings: in these insects there are two types, the first ones are known as tegmina. They are leathery and function to protect the back wings. These secondary ones wings are membranous are more directly used for flight. Tegmina are variable in the presence of a venation, which is used to identify groups. In male crickets, the stridulator organ is usually located here. The true wings (hind wings) also vary, although they are usually transparent. In some groups they have colors or spots and they differ in sizes. All these aspects are used for the respective classifications.
- Hearing organ: another difference between crickets and grasshoppers has to do with their hearing ability. In grasshoppers, auditory organs known as tympana are located on the sides of the abdomen. These thin membranes vibrate to produce their characteristic sounds. This structure is not always present in crickets, but it is always located on the anterior tibiae if so.
- Reproductive organs: the last difference between grasshoppers vs. crickets is their sexual organs. Both female grasshoppers and crickets have an ovipositor organ with two pairs of valves for depositing eggs, but this is generally longer in grasshoppers. Both male grasshoppers and crickets have an intromittent organ which is a phallic structure that is sclerotized, i.e. hardened for better protection. Crickets tend to be a little more sclerotized than grasshoppers, but this will depend on species.
Now that you know the difference between crickets vs. grasshoppers, let's see what else makes these insects so special.
Other differences between grasshopper vs. cricket
In addition to the above, there are other differences between grasshoppers and crickets that can be used to help us tell them apart from each other:
- Taxonomy: not only do each species of cricket and grasshopper have different common names, they are grouped into different suborders. Crickets are located in Ensifera and grasshoppers in Caelifera. If you want to know more about them, check out this post on the different types of crickets.
- Evolution: grasshoppers are estimated to be older than crickets in terms of evolutionary history. In fact, they older than many other insect types.
- Species: there are more species of grasshoppers than crickets, with some 9000+ species of crickets identified, but 11000+ grasshopper species currently known to science.
- Population distributions: crickets are distributed throughout the world, except in very cold areas. Grasshoppers also have a wide distribution, but thrive best in dry areas.
- Groups: another difference is that grasshoppers under certain environmental conditions can have bodily changes. They are also known to group together in large numbers of individuals. In these cases they are known as locusts and become crop pests. This does not happen with crickets.
- Diet: crickets have a more varied diet, some are herbivorous and others are omnivores. They can become predators in certain cases. Grasshoppers are much more commonly herbivores.
- Activity periods: crickets are more nocturnal, while grasshoppers are diurnal. We may find exceptions, but this is the general trend in both insect types.
- Coloration: although both groups have camouflage strategies, in crickets we find darker colors, while in various species of grasshoppers brighter colors. Learn more about the difference between camouflage and mimicry in animals.
- Jumping: grasshoppers are better jumpers than crickets.
Learn more about the life cycle of grasshoppers with our article on how long do grasshoppers live?
If you want to read similar articles to Grasshopper vs. Cricket Differences, we recommend you visit our Facts about the animal kingdom category.
- Aguirre, A. and Barranco, P. (2015). Order Orthoptera. Retrieved from: http://sea-entomologia.org/IDE@/revista_46.pdf
- Hickman, C., Roberts, L., & Parson, A. (2000). Comprehensive principles of zoology. McGraw Hill Inter-American.
- ITIS. (2024). Ensifera. Retrieved from: https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=102231#null
- ITIS. (2024). Caelifera. Retrieved from: https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=102161#null