How to Tell the Difference Between Male and Female Betta Fish


Betta fish, also known as Siamese fighting fish, are one of the most popular aquarium fish in the world. They are known for their beautiful colors and elaborate fins. Betta fish are also relatively easy to care for, making them a good choice for both experienced and beginner fishkeepers. However, one thing that can be confusing for new betta fish owners is how to tell the difference between male and female betta fish.
In this AnimalWised article, we will take a closer look at the key differences between male and female betta fish so that you can easily identify the sex of your fish.
Types of betta fish
The betta fish, also known as the Siamese fighting fish, is a small, freshwater fish that is native to Southeast Asia.
Betta fish are typically between 5 and 7.5 centimeters (1.9 and 3 inches) long when fully grown. They have long, flowing fins and a variety of different colors and patterns. Some of the most popular colors include red, blue, green, and yellow. Betta fish can also have a variety of different patterns, such as solid color, bicolour, multicolor, marble, and butterfly.
Here are some of the most common types of betta fish:
- Veiltail betta: these are the most common type of betta fish. They are known for their long, flowing fins that resemble a veil.
- Halfmoon betta: these fish have large, semicircular tail fins that resemble a half moon when fully spread.
- Crowntail betta: these fish are easily recognizable due to their unique fins, which have elongated and separated rays that give them a spiky appearance that resembles a crown.
- Double tail betta: double tail bettas have a split caudal fin, creating the illusion of two tails.
- Plakat betta: they are short-finned bettas that resemble wild betta fish. They are known for their vibrant colors and active nature.
Despite the wide variety of betta fish types, the differences between males and females are relatively consistent across all types.
Learn how to create a thriving aquarium for your betta fish by reading this other article.

Characteristics of male betta fish
Identifying the gender of Betta fish, also known as Siamese fighting fish, can be an essential skill for aquarists, especially when planning to breed or when selecting a vibrant and visually striking addition to your aquarium.
Male and female betta fish have some common features, but several physical and behavioral characteristics can help you determine which you have.
Physical appearance
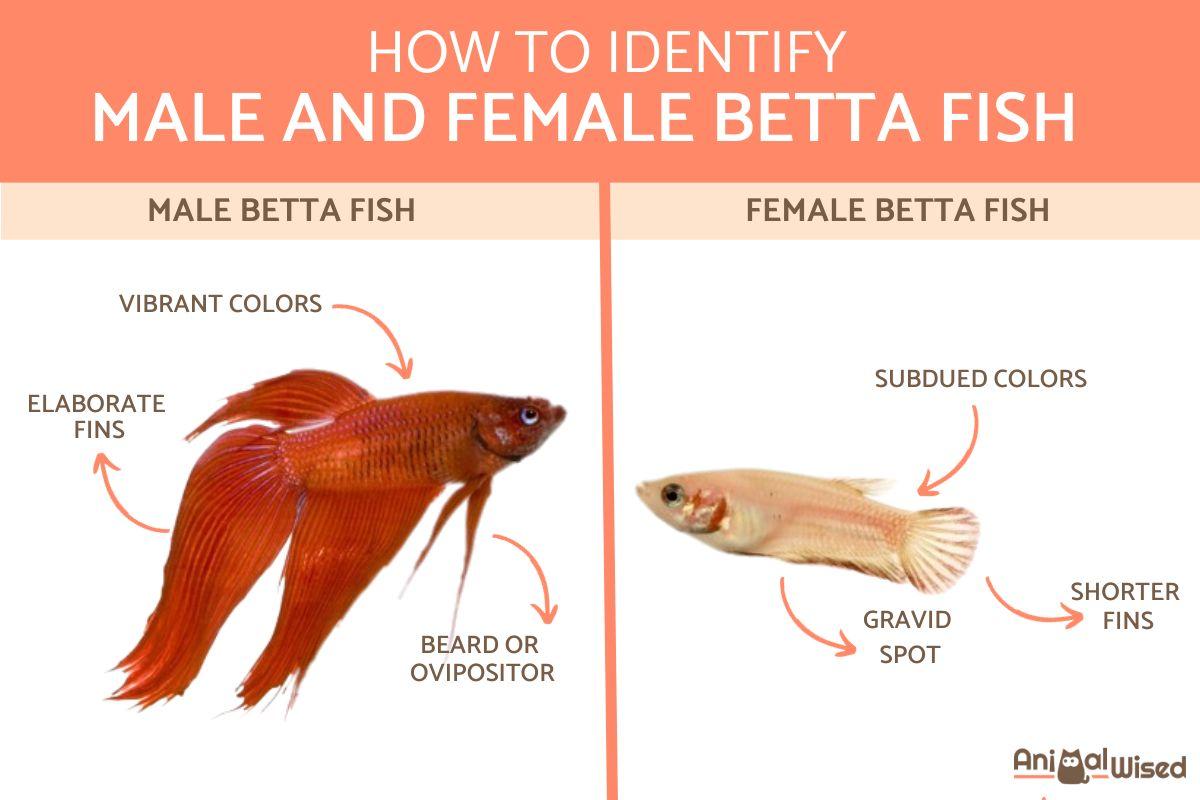
- Vibrant colors: male Betta fish are renowned for their stunning and vibrant colors. They often display more intense and varied hues compared to females. Look for deep, rich shades of blue, red, green, and combinations of these colors.
- Elaborate fins: males have elaborate and eye-catching finnage. Their dorsal, caudal, and anal fins are more extended and flamboyant. The caudal fin, in particular, often features intricate patterns and can be quite large.
- Fins with edges: male Betta fins have distinct edges. Their dorsal and anal fins may appear pointed or elongated, and the caudal fin might have decorative rays or webbing that form unique shapes.
- Beard or ovipositor: the ventral fins of male Bettas usually feature a small, white, and pointy protrusion known as a beard or ovipositor. This structure is absent in females and is used by males for various purposes, including courtship and aggression.
- Longer and slender body: male Bettas typically have a more elongated and slender body shape compared to females, which have shorter and rounder bodies.
Behavior
- Bubble nest building: males have a natural instinct for building bubble nests on the water's surface. These nests are created from clusters of small bubbles held together by saliva. Bubble nests are used by male fish to attract females and to protect their eggs and fry. If your Betta is constructing a bubble nest, it's almost certainly a male.
- Aggressive behavior: male Bettas are notorious for their territorial and aggressive nature. They will often flare their fins, display vivid colors, and engage in confrontations with other males. This aggressive behavior is less common in females.
- Mirror test: if you place a mirror near your Betta's tank, a male Betta will often react aggressively by flaring its fins and showing off its colors. This behavior is an instinctive response to what it perceives as a rival male.
Being able to identify the sex of betta fish is essential for providing proper care and ensuring the well-being of all fish in the aquarium. If you are still unsure of the sex of your betta fish, you can consult with a veterinarian or experienced fish keeper. They will be able to help you identify the sex of your fish and provide additional care advice.
You might be interested in this other article, where we explain why betta fish puff up and how to ensure their health and well-being.

Characteristics of female betta fish
While male and female Bettas share some common traits, distinguishing a female from her male counterpart requires a keen eye. Here's a guide to identifying a female Betta fish:
Physical appearance
- Subdued colors: unlike their male counterparts, female Betta fish generally exhibit more subdued and less intense colors. They tend to have shades of blue, red, or brown, often with subtle hues and fewer variations.
- Shorter fins: female Bettas typically have shorter and less elaborate finnage. Their dorsal, anal, and caudal fins are smaller and less flamboyant compared to males. The caudal fin may be rounder, but it lacks the intricate patterns seen in males.
- Lack of beard: female Betta fish do not possess the white, pointy protrusion known as a beard or ovipositor, which is present in males. This distinctive feature in males is used for various purposes, such as courtship and aggression.
- Rounder body: female Bettas tend to have rounder and shorter bodies compared to the longer, slender bodies of males.
- Gravid spot: a gravid spot, also known as an ovipositor, is a small, dark spot located behind the ventral fins. It's a distinctive feature of female Betta fish and becomes more visible when they are carrying eggs. However, this spot is not always present, and it may be more noticeable during the breeding season.
Behavior
Female betta fish are generally more peaceful and less aggressive than male betta fish. You can observe this difference in behavior by observing a group of each sex. Female betta fish are more likely to school together, display less fin flaring, and engage in fewer conflicts. They are also less likely to react to a mirror held near their tank.
Female betta fish do not typically construct bubble nests, but they may exhibit other behaviors when preparing to lay eggs, such as searching for suitable surfaces or sheltered spots to deposit their eggs. This is known as nesting behavior.
Other nesting behaviors that female betta fish may exhibit include:
- Fanning their fins near the surface of the water to create a current.
- Blowing bubbles on plants or other objects.
- Circling around potential nesting sites.
- Rubbing their bodies against potential nesting sites to clean them.
If you want to read similar articles to How to Tell the Difference Between Male and Female Betta Fish, we recommend you visit our What you need to know category.
- Betta Fish Anatomy: External&Internal Explained . Betta Fish. Available at: https://bettafish.org/betta-fish-anatomy/.
- ARBOLEDA OBREGÓN, DA (2006). Breeding and production of Betta (Betta splendens) for non-professional aquarists. In: REDVET Veterinary Electronic Magazine . V. VII, no. 4. ISSN 1695-7504. Available at: http://www.veterinaria.org/revistas/redvet/n040406/040610.pdf.
- GARCÍA ALVES, L. (2008). Effect of species and color of opponents on the aggressiveness of male Betta splendens . University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria: Faculty of Marine Sciences.