Jawless Fish - Characteristics And Examples


Agnatha are fish that have existed for over 470 million years. Although most agnatha are now extinct, some have found unique and interesting ways to survive. Agnatha or jawless fish can be found in waters all over the world, and they share few characteristics with other marine mammals.
But, what is a jawless fish? Keep reading here to find out! In this AnimalWised article we’ll be discussing the most common characteristics and examples of agnatha, images included.
- What is Agnatha?
- Jawless fish characteristics
- Jawless fish examples: lamprey
- Sea lampreys
- River lampreys
- Lamprey examples
- Jawless fish examples: hagfish
- Hagfish species
- Hagfish examples
- Extinct jawless fish: Ostracoderm
What is Agnatha?
Now, what is a jawless fish (Agnatha)? Agnatha species, or jawless fish, are said to be the earliest vertebrates ever recorded, that are believed to be present during the Paleozoic era. In fact, the evolution of fishis claimed to have begun with jawless fish. Jawless fish appeared on the planet 470 million years ago and started becoming extinct 370 million years ago, although some species have still managed to survive.
In which class are jawless fish found?
Agnatha is a superclass within the phylum Chordata. This group consists of cyclostomes (Lamprey and hagfish), that are still alive today, and extinct species, conodonts and ostracoderms.
Class agnatha are the third group included in the common classification of fish. Following agnatha revolution we have cartilaginous or chondrichthyes (Chondrichthyes), such as rays, sawfish, electric rays and sharks. Then came bony fish (Osteichthyes), which are a group that includes all those species that have gills and bladder.
For more, we suggest taking a look at our article where we discuss the 5 oldest animals in the world: ancient extant species.
Jawless fish characteristics
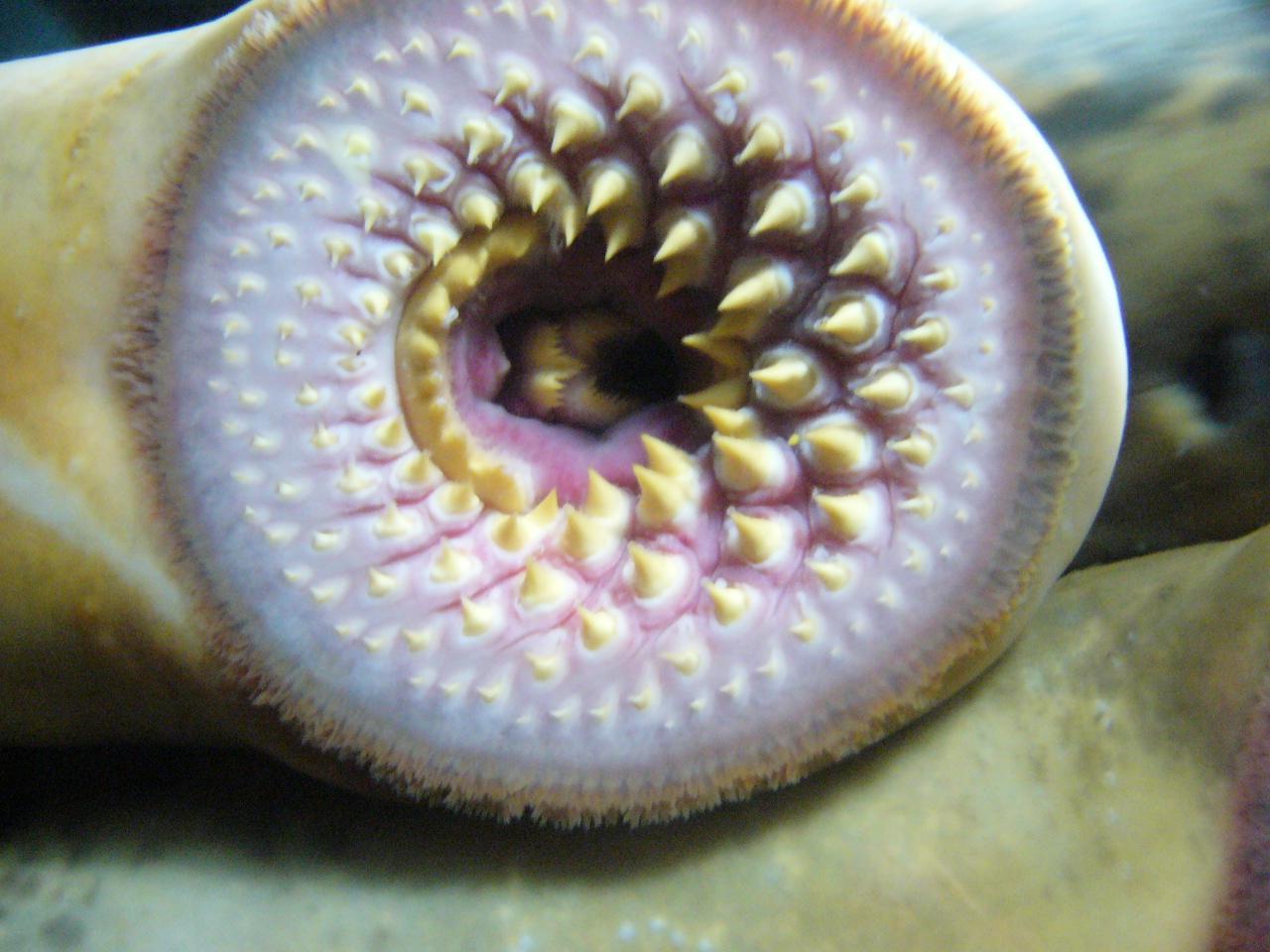
What are the main agnatha characteristics? In ancient times, although all agnatha shared the same verterbrate class, agnatha morphology was varied. In general, however, agnatha species is a species which is characterized by an absence of jaws. This species also carried a cartilaginous skeleton and possessed external structures similar to that of armor.
One of the most common agnatha characteristics is that they resemble the eels of today, with an elongated slimy body lacking scales and fins. Their cartilaginous skeleton lacks an occipital region, and its gills are shaped like a sac.
Agnatha, a type of fish, are ectothermic. Agnatos parasitizes other fish species, or they feed on carrion through a suction method. At present, there are two surviving jawless agnatha fish, lampreys (41 varieties) and the hagfish (31 varieties).
For more, read about the types of freshwater fish.
Jawless fish examples: lamprey
Hyperoarties (Hyperoartia) are jawless primitive fish commonly known as lampreys. The lamprey body is very similar to that of eels; elongated, flexible and thin. Lampreys are born in freshwater areas, and as they mature, they go to the sea. Lampreys return to freshwater to mate. This process does, however, depending on the subspecies.
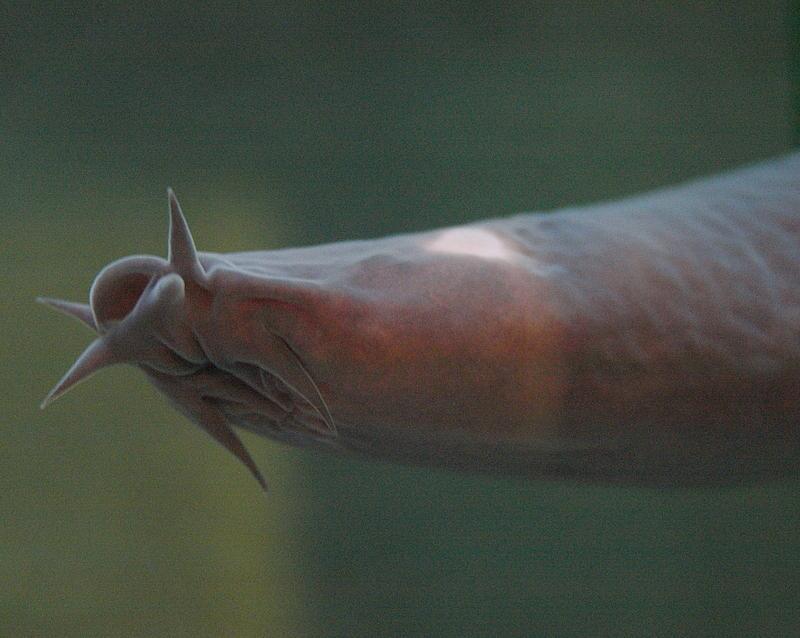
A lamprey’s mouth is circular and full of suckers, which adheres to parasitic species such as sharks and marine mammals. Within its mouth, a lamprey has conical teeth and a tongue (adapted to scrape tissue). These structures allow the lamprey to feed on prey and suck on blood and bodily fluids, its main sources of food. Male lampreys have two fins while female only have one.
The two most common lamprey species include the sea lamprey and river lamprey.

Sea lampreys
The most common sea lamprey species include:
Chilean lamprey (Mordacia lipicida)
The Chilean lamprey is an endemic agnato fish to the coast of Chile. It measures up to 54 cm in length with a pouch that runs from its cervical to its gills, in addition to a large eye located in its lateral-dorsal region.
During the winter, the Chilean lamprey moves away from the colder coasts and migrates deeper into the sea.
Image below: Chilean lamprey
Pouched lamprey (Geotria australis)
The pouched lamprey inhabits the Indian, Pacific and Atlantic ocean. This agnatha species measures up to 60 cm in length and develops a pouch under its eyes during mating season, designed to aid it in building a nest.
This species of lamprey feeds on teleost fish. Despite spending most of its life in the sea, the pouched lamprey approaches nearby rivers to lay eggs during mating seasons.

River lampreys
Several species of lampreys spend a large part of their life cycle in rivers, while others only inhabit these fresh waters at specific times. Predominant river lamprey species include:
European river lamprey (Lampetra fluviatilis)
The European river lamprey is a jawless fish species that measures up to 40 cm in length and can be found distributed along European rivers, where it spends most of its life. Once these lampreys reach adulthood, they move to nearby oceans and seas.
The European river lamprey has 7 holes that function as gills, as well as two developed eyes. They have sharp teeth which allow them to feed on fish.
Brook lamprey (Lampetra planeri)
The brook lamprey is similar to te European river lamprey, but smaller. This jawless fish species can be found in the Spanish community of Narrava and in some rivers of Portugal.
An interesting fact about the brook lamprey is that its larvae takes 6 years to reach sexual maturity. During this period, they feed on algae and debris found on riverbeds.

Lamprey examples
Additional agnatha lamprey species include:
- Australian brook lamprey (Mordacia praecox)
- Short-headed lamprey (Mordacia mordax)
- Sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus)
- Pacific lamprey (Lampetra tridentata)
- Ohio lamprey (Ichthyomyzon bdellium)
- Caspian lamprey (Caspiomyzon wagneri)
- Carpathian brook lamprey (Eudontomyzon danfordi)
- Vladykov’s lamprey (Eudontomyzon vladykovi)
Jawless fish examples: hagfish
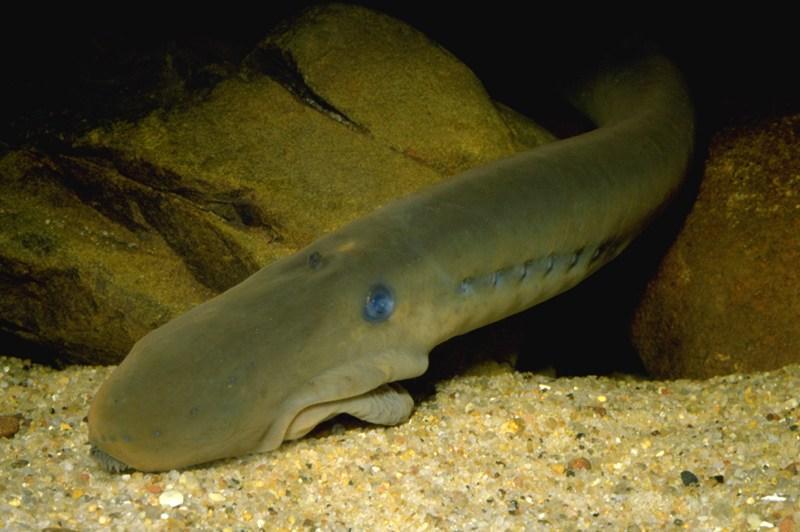
The hagfish (Myxini) are another extant class of agnatha or jawless fish. Like lampreys, hagfish have a long circular body covered with a mucous-y layer. Their general appearance is very primitive. They do not have taste sensory organs, but do have receptive cells in their skin, as well as simple eyes.
Hagfish feed on carrion and the viscera of larger animals, which they gnaw at. Hagfish species, despite having no jaw, have a rudimentary snout, in addition to a tongue capable of scraping away at skin.

Hagfish species
Among the species of hagfish that exist today, we have the:
Goliath hagfish (Eptatretus goliath)
The Goliath hagfish it is known by a single sighting made in New Zealand, where this species is endemic. The only known fact about this hagfish is that it lives at 811 meters deep and is 1 meter long.
Atlantic hagfish (Myxine glutinosa)
The Atlantic hagfish lives in waters surrounding the Iberian Peninsula, Norway, Canada, Mexico and the United Kingdom, where it can be located between roughly 40 and 1100 meters deep.
This jawless fish species can reach up to 1 meter in length and is nocturnal. Additionally, the Atlantic hagfish feeds on dead or dying animals by entering the body and feeding on the viscera.

Hagfish examples
In addition to those mentioned above, other hagfish species include:
- Southern hagfish (Myxine australis)
- White-headed hagfish (Myxine ios)
- Cape hagfish (Myxine capensis)
- Garman’s hagfish (Myxine garmani)
- Dwarf hagfish (Myxine pequenoi)
- Whiteface hagfish (Myxine circifrons)
- Jespersen’s hagfish (Myxine jespersenae)
- Caribbean hagfish (Myxine mcmillanae)
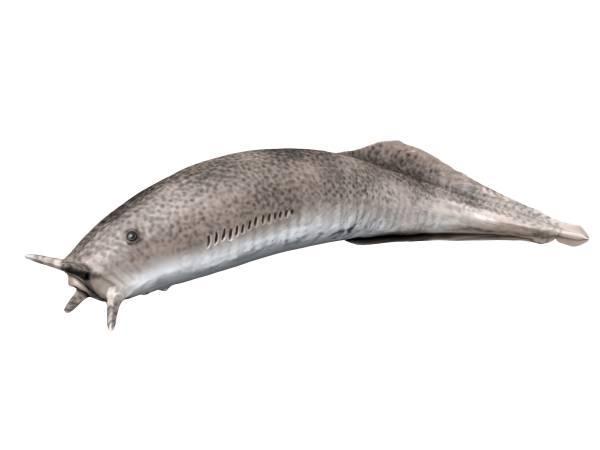
Extinct jawless fish: Ostracoderm
When it comes to extinct Agnatha class fish, ostracoderms (Ostracodermi) are among the best known. These agnatha used to measure between 50 and 60 cm long and became extinct 350 million years ago.
Ostracoderms were different compared to other jawless fish as they had thick scales that formed a bone shield, protecting them from predators. These agnathas are among the first vertebrates that appeared on planet Earth. Although current extant agnatha are cartilaginous and have a non-skeletal skeleton, they are also considered chondrichthyans.

If you want to read similar articles to Jawless Fish - Characteristics And Examples, we recommend you visit our Facts about the animal kingdom category.
- Rodríguez, A.; Bessonart, M. (2007). Agnatos y condrictios. Facultad de Ciencias.
- Granado Lorencio, C. (2002). Ecología de peces. Universidad de Sevilla.
- Mincarone, M.M. (2011). Eptatretus goliath. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: e.T196023A8994230. Disponible en: http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2011-1.RLTS.T196023A8994230.en.
- Mincarone, M.M. (2011). Myxine glutinosa. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: e.T196057A8988080. Disponible en: http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2011-1.RLTS.T196057A8988080.en.