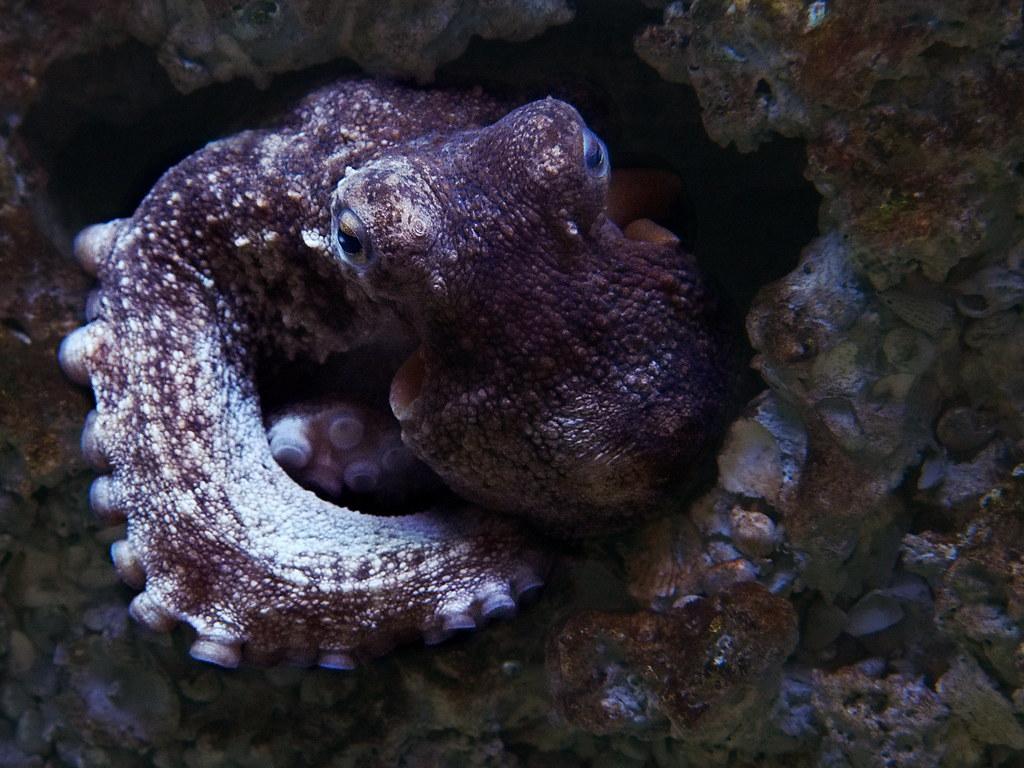
Types of Mollusks - Characteristics And Examples


Mollusks refer to are a large group of soft-bodied invertebrate animals. Although the phylum Mollusca are made up of a set of incredibly diverse animals, there are certain characteristics which aid to classify them. Whether you are looking to discover mollusks characteristics, classification of mollusca and/or information about all types of mollusks, this article is for you.
Keep reading here at AnimalWised to discover everything you need to know about mollusks, photos included!
- Mollusk definition
- Mollusc or mollusk
- Mollusks characteristics
- Classification of mollusca
- Mollusca examples
- Chaetoderma elegans
- Neomenia carinata
- Sea cockroach (Chiton articulatus)
- Antalis vulgaris
- Wedge clam (Donax trunculus)
- European flat oyster (Ostrea edulis)
- Garden snail (Helix aspersa)
- Common octopua (Octopus vulgaris)
- Marine molluscs
Mollusk definition
Mollusks are invertebrates whose integumentary system is soft like annelids. There are some which carry a protective shell, while others do not. Mollusks are the second largest group of invertebrate animals after arthropods. There are roughly 100,00 species of mollusks, of which 60,000 are gastropods. The amount of fossil species estimates at roughly 30,000.
The majority of mollusks include benthic sea mollusks, which means that they live on seabeds. Many others are terrestrial, like snails. The great diversity that exists within the phylum Mollusca have colonized a multitude of different habitats and, therefore, feeding depends largely on the species and their environment.
For more, we recommend reading our article where we discuss the different types of snails, including marine and terrestrial.

Mollusc or mollusk
Before we begin with the different types of mollusks characteristics, and classification of mollusca, let’s look at the defining word itself. Do we say types of molluscs or types of mollusks? Well, it depends, but both are correct.
When we define animals of the phylum Mollusca, there are two different types of spelling. Mollusk is generally preferred in American English, while mollusc is more commonly used in British English.
Mollusks characteristics
Mollusks are a very diverse group of invertebrate animals, and finding common characteristics among all of them can be slightly tricky. Therefore, here we present some of the most common characteristics among mollusks, but bear in mind, there are some exceptions:
A mollusk body is divided into four main areas:
- Mantle: refers to the dorsal surface of the body that can secrete protection. This protection has a chitinous and protein origin that subsequently creates calcareous deposits, spicules or a shell. Animals that do not have a shell generally have chemical defenses.
- Locomotor foot: is ciliated, muscular and include mucous glands. This ‘foot’ carries several pairs of dorsoventral muscles that serve to retract the foot and attach it to the mantle.
- Cephalic zone: which includes the brain, mouth and other sensory organs.
- Paleal cavity: where the osphradium (olfactory organs), body orifices (anus) and gills are located.
Mollusk digestive system some characteristic features:
- Stomach: they follow extracellular digestion. This means that the digestible particles are selected by the digestive gland (hepatopancreas) and, the rest, pass into the intestine and form stool.
- Radula: is an organ located inside a mollusk’s mouth, this membrane is formed in the shape of a tooth, supported by the odontophore (mass of cartilaginous consistency) and moved by complex musculature. The chitinous teeth that the radula presents tear food. Old and worn out teeth fall out and new ones form in the radular sac. Many solenogastres (mollusk subclass) lack radula. Additionally, bivalve, a class of marine and freshwater molluscs, have no radula.
When it comes to a mollusk circulatory system, only the heart and the nearest organs have vessels. A mollusk heart is divided into two atria and a ventricle. They carry metanephrids which collaborate with the ultrafiltration heart, and produces primary urine which will reabsorb the nephrids that also regulate the amount of water in the body. A mollusk’s reproductive system has two gonads in front of the pericardium. Gametes are evacuated to the paleal cavity, mostly attached to the nephrids. Mollusks can be classified as dioecious or hermaphroditic.
For more, we recommend reading our article where we list and discuss the major groups of invertebrate animals.
Classification of mollusca
Mollusk classification is divided into eight classes, all of them living. Mollusk classification include:
- Class Caudofoveata: includes molluscs shaped like worms. They have no shell, but their body is covered with calcareous and aragonitic spicules. They live buried in the ground with their heads down.
- Class Solenogastres: are very similar to the previous class, so much so that they were previously included in the same group. They also carry a worm shape, but instead of living buried in the ground, they move freely in the ocean and feed on cnidaria. They also have calcareous and aragonitic spicules.
- Class Monoplacophora: include very primitive mollusks. Their body is covered by a single shell,resembling clams, but they have a muscular foot like snails.
- Class Polyplacophora: at first glance, this group of mollusks are similar to a type of crustacean. Its body is covered by a set of plates reinforced with magnetite. They also have a crawling muscular foot and a radula.
- Class Scaphopoda: these mollusks have a very elongated body like their shell, which is shaped like a horn. These are also known as fang shells. This is one of the best known types of marine mollusks.
- Class Bivalve: are aquatic mollusks whose body is enclosed between two leaflets or shells. These two leaflets are able to close thanks to set muscles and ligaments. The most well-known types of bivalve mollusks include clams, mussels or oysters.
- Class Gastropoda: gastropods include snails and slugs, both terrestrial and marine species. They have a well differentiated cephalic area, a muscular foot that serves to crawl and/or swim as well as a shell on the back. This shell may be absent in some species.
- Class Cephalopoda: this class made up of octopuses, cuttlefish, squid and nautilus and, surprisingly, all carry a shell. The most obvious is that of the nautilus, whose shell is external. Sepias and squid have an internal shell which varies in size. The octopus shell is almost vestigial, and only has two thin calcareous strands present inside the body. Another important characteristic of cephalopods is that their muscular foot (present in molluscs) are tentacles. Cephalopods can carry between 8 to more than 90 tentacles, depending on the species.
Mollusks without a shell
Three types of mollusks without a shell include; banana slugs, quid and octopi.
For more, you may be interested in reading our article where we list the most common types of seashells.
Mollusca examples
Now that we’ve covered Mollusca characteristics and classification of mollusks, let’s take a look at both marine mollusks and terrestrial mollusk types:
1. Chaetoderma elegans
This species of glisten worm, is shaped a mollusk without a shell. This type of mollusk belongs to the class Caudofoveata. This marine molluscs species is tropically distributed in the Pacific Ocean. It can be found at depths of 50 meters to more than 1800 meters.
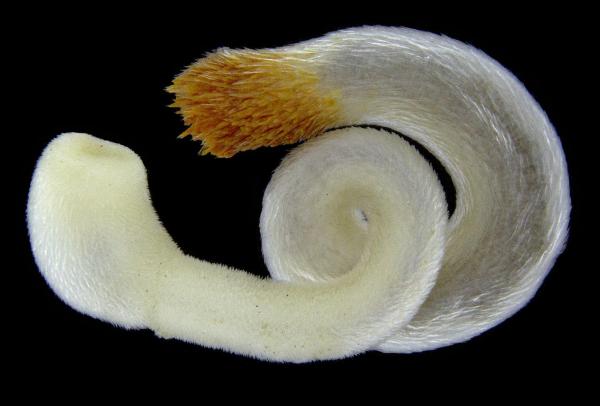

2. Neomenia carinata
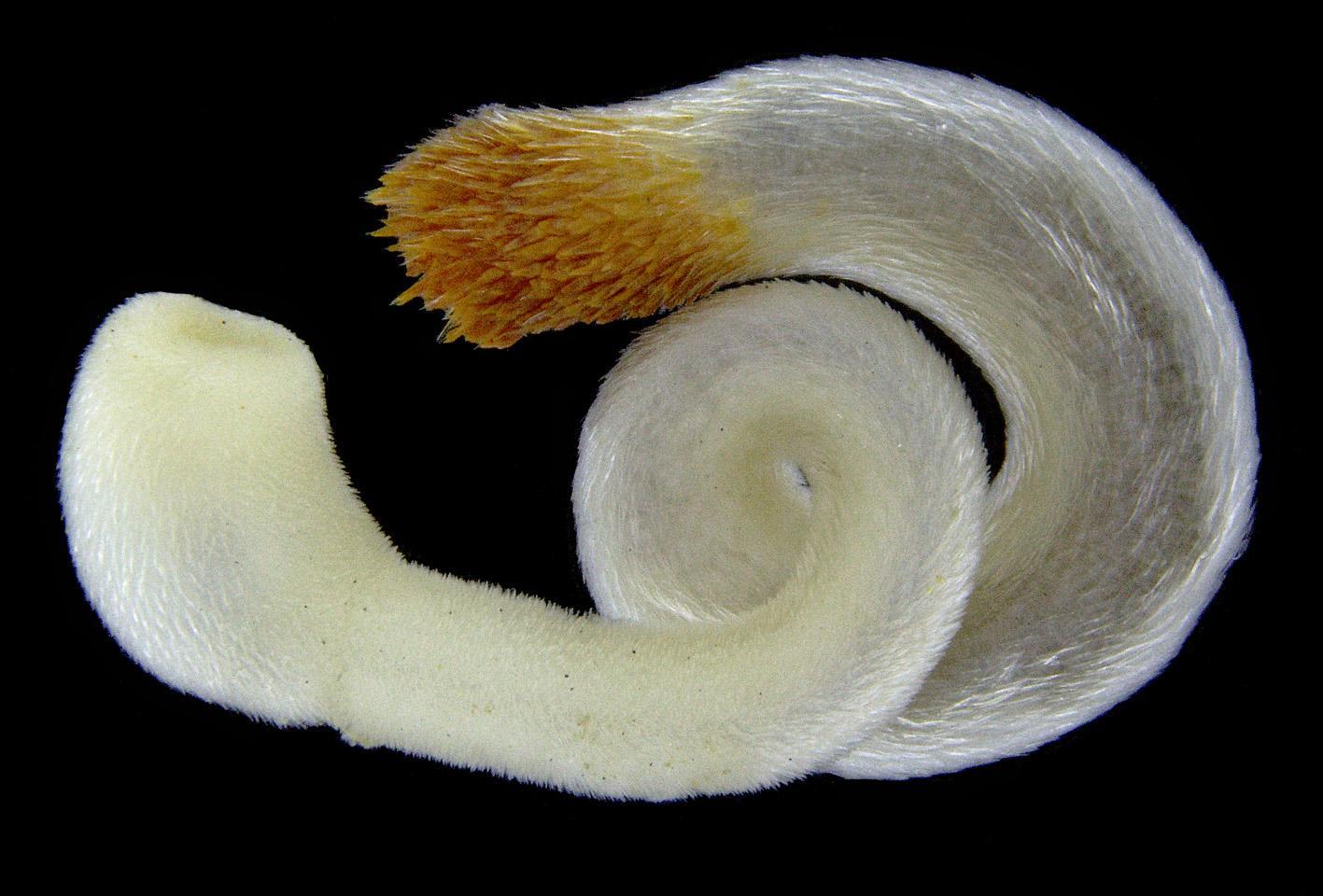
The Neomenia carinata is another vermiform mollusks without a shell, but belongs rather to the Solenogastres family. This mollusk type can been found in a depth range of between 10 and 565 meters and lives freely in the Atlantic Ocean, on the coasts of Portugal.
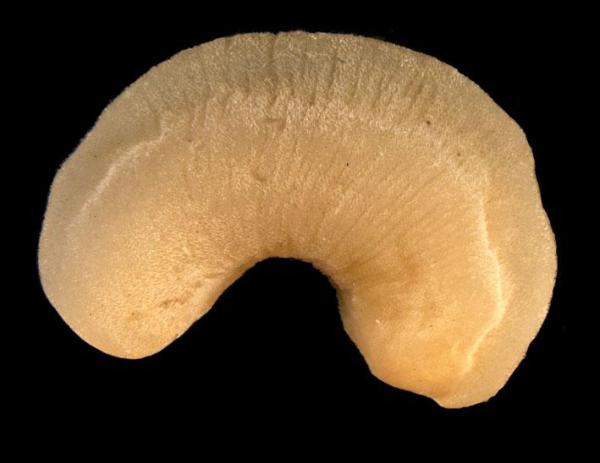
3. Sea cockroach (Chiton articulatus)
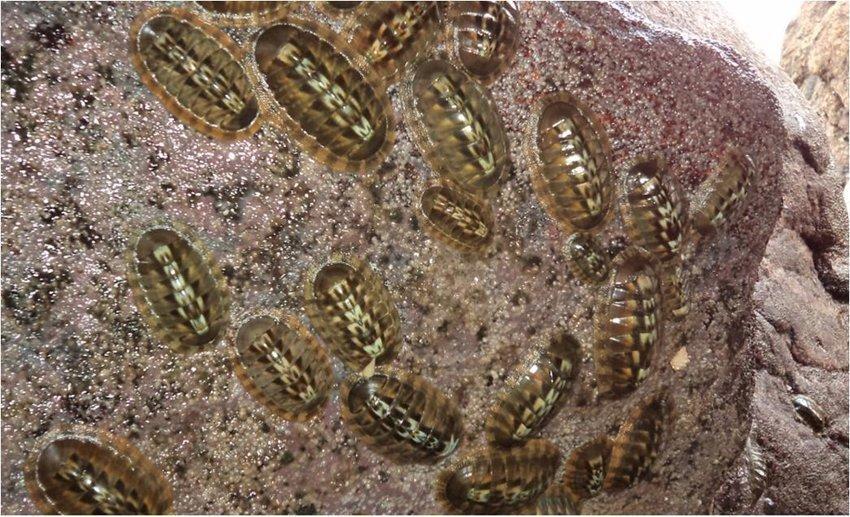
The sea cockroach is a kind of endemic Polyplacophora marine mollusk from Mexico. It lives on the rocky substrate in intertidal zones. It is a large species, able to reach 7.5 centimeters in length.

4. Antalis vulgaris
It is a species of Scaphopoda marine mollusk with a tubular shell or fang-shaped shell. This white mollusk lives in sandy and muddy substrates at shallow depths in intertidal zones. They can be found along the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts.
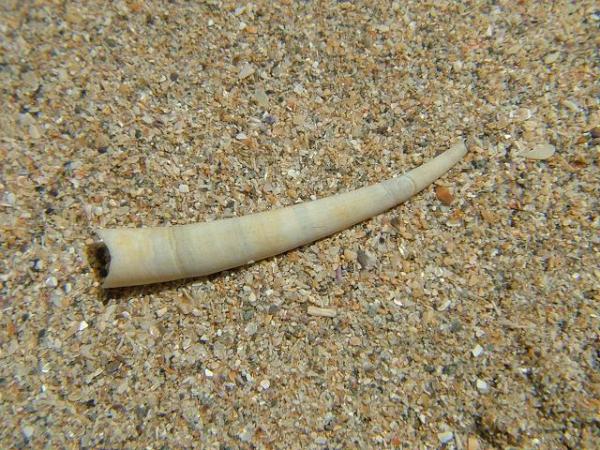

5. Wedge clam (Donax trunculus)
This Bivalve species, also referred to as the abrupt wedge shell or wedge clam, is a small marine mollusk that lives on the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts. They are also considered edible mollusks, and are greatly appreciated in the local culinary culture. Wedge clams can live in the subtidal areas of about 20 meters deep.
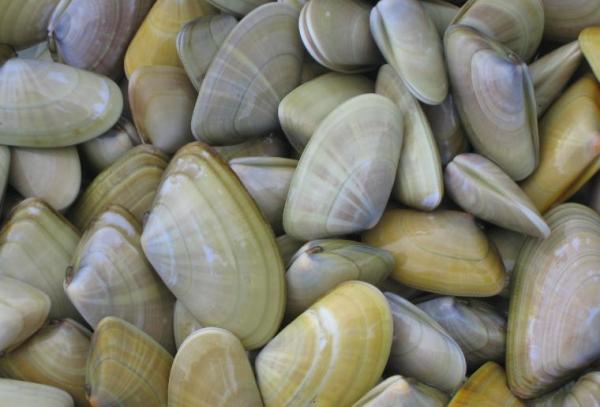

6. European flat oyster (Ostrea edulis)
Oysters are one of the types of Bivalve marine mollusks of the order Ostreoida. This species can measure up to 11 centimeters and produce pearls. Oysters are distributed from Norway to Morocco and the Mediterranean. In addition, they are cultivated in aquaculture and are a popular edible mollusk.
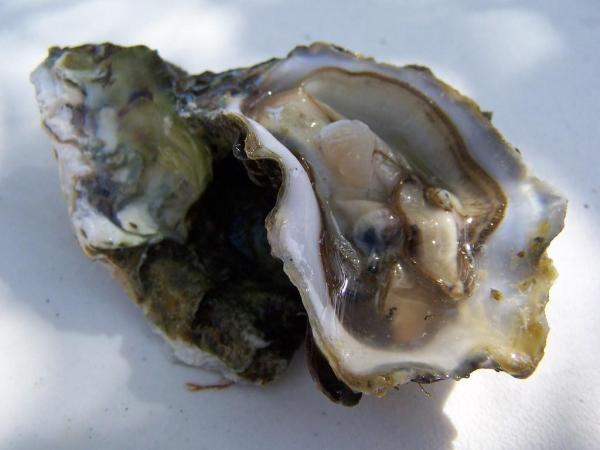

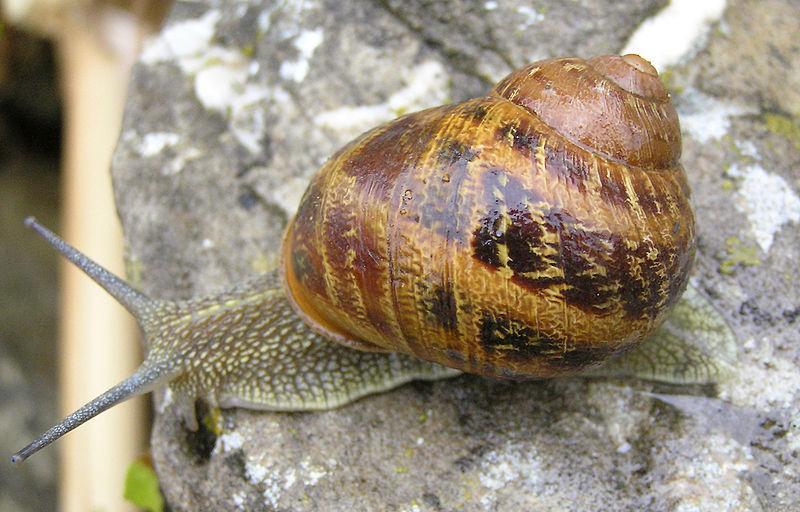
7. Garden snail (Helix aspersa)
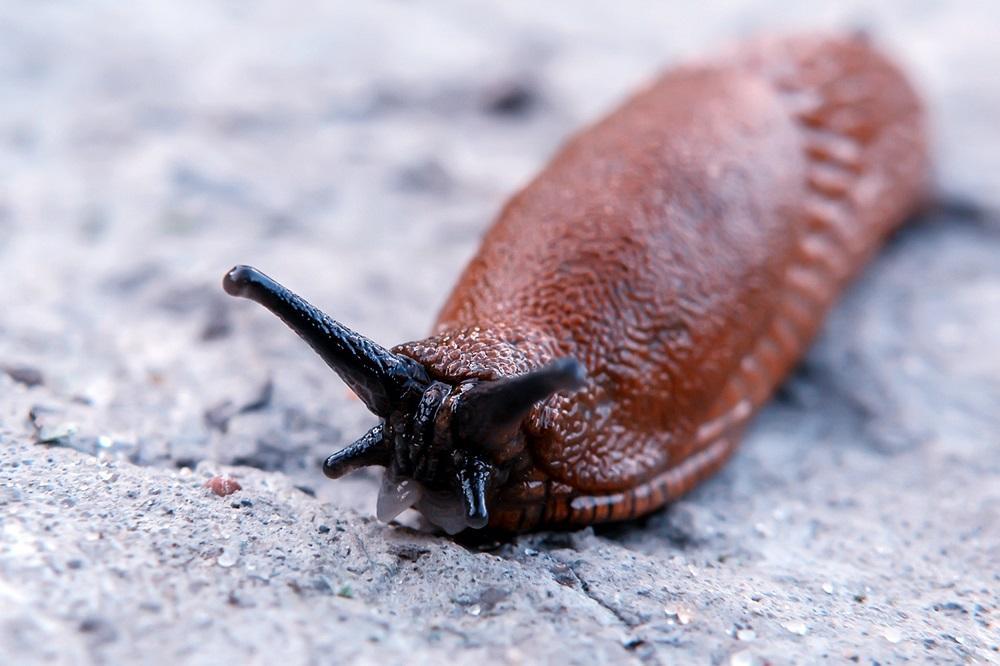
The common snail is a species of Gastropod terrestrial mollusk that follows pulmonary respiration. This means that they have no gills and live on the earth’s surface. Garden snails require a lot of moisture, and if they do not receive it, they hide in their shells to avoid drying out.
For more, read about animals with exoskeleton.

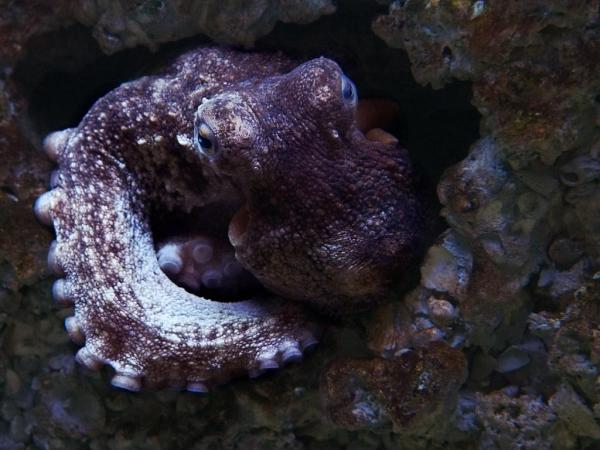
8. Common octopua (Octopus vulgaris)
The common octopus is a Cephalopod marine mollusk that lives in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. They can measure up to about a meter in length and can change color thanks to chromatophores in their body. Octopus are also a common edible mollusk, popular in gastronomy.

Marine molluscs
Looking for more? Here are some additional mollusk types:
- Scutopus robustus
- Scutopus ventrolineatus
- Laevipilina cachuchensis
- Laevipilina Rolani
- Tonicella lineata
- West Indian fuzzy chiton (Acanthopleura granulata)
- Ditrupa arietina
- Freshwater pearl mussle (Margaritifera margaritifera)
- Cockscomb pearl mussel (Cristaria plicata)
- Iberus gualtieranus alonensis
- Iberus gualtieranus gualtieranus
- Giant African snail (Achatina fulica)
- Common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis)
- Giant squid (Architeuthis dux)
- Giant Pacific octopus (Enteroctopus dofleini)
- Palau Nautilus (Nautilus belauensis)
If you want to read similar articles to Types of Mollusks - Characteristics And Examples, we recommend you visit our Facts about the animal kingdom category.
- Liuzzi, María Gabriela. (2014). Polyplacophora.
- MolluscaBase (2019). WoRMS Mollusca: MolluscaBase (version 2019-03-06).
- MolluscaBase (2019). MolluscaBase. Neomenia carinata Tullberg, 1875.
- Urgorri, V., Díaz-Agras, G., García-Álvarez, O. & Señarís, M.P. (2017). Filo Mollusca, Clase Polyplacophora. In: BAÑÓN, R. (Ed.). Inventario de la biodiversidad marina de Galicia: Proyecto LEMGAL. Consellería do Mar, Xunta de Galicia, Santiago de Compostela. pp. 269-272. ISBN: 978-84-453-5293-9.














