Scavenger Birds - Types and Characteristics


Scavenger birds are a diverse group of birds that feed on carrion, or dead animals. They are important members of ecosystems, playing a vital role in nutrient cycling and disease control. Scavenger birds can be found in all parts of the world, from the tropics to the Arctic. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes, from the small and nimble shrike to the large and powerful vulture.
The upcoming AnimalWised article delves into scavenger birds, exploring their primary characteristics and the various types within this category.
What are scavenger birds?
Scavengers are a diverse group of birds that play a crucial role in ecosystems by consuming and recycling the remains of deceased animals.
Scavenger birds are found on every continent, and their distribution often depends on the availability of carrion and suitable habitats. These birds often hold cultural significance in various societies. In some cultures, vultures are seen as symbols of purification and are associated with death and rebirth.
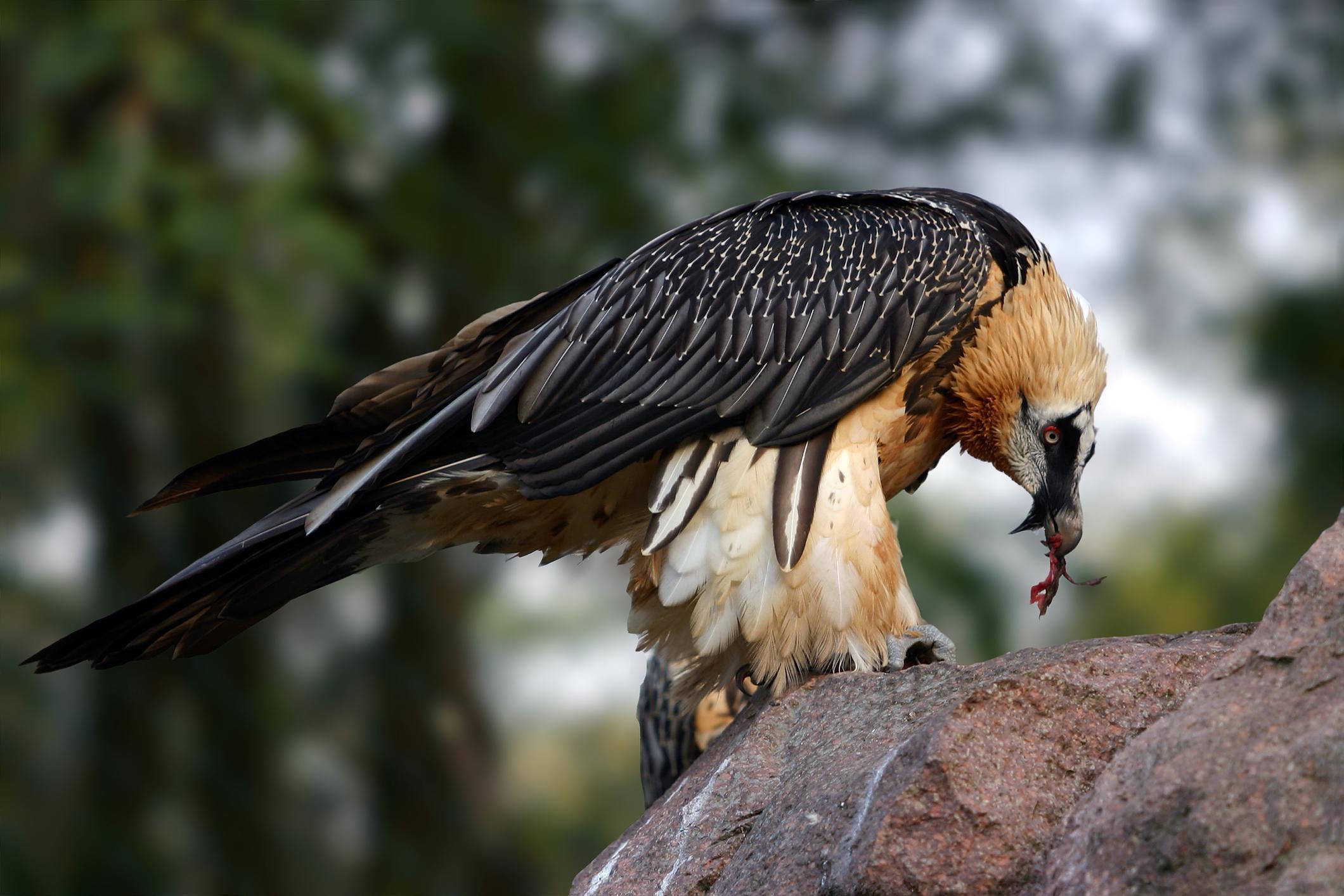
Scavengers, unlike predators that actively hunt and kill their prey, have evolved remarkable adaptations that enable them to locate and efficiently feed on carcasses. These birds possess strong, hooked beaks perfectly suited for tearing flesh, and their sharp, powerful talons allow them to grip and hold onto carcasses securely.
Keen eyesight is an essential asset for scavenger birds, enabling them to spot carrion from long distances. Some species, such as vultures, have been known to detect carcasses from several miles away. Additionally, scavenger birds boast a well-developed sense of smell, which they utilize to locate carrion hidden from view.
Scavenger birds fill an essential ecological niche, contributing to the cleanup of the environment by removing and recycling dead animal matter. This scavenging behavior helps prevent the spread of diseases, maintains a balance in ecosystems, and ensures that nutrients are returned to the environment in the form of decomposed organic matter.
Continue your exploration of the fascinating world of scavengers by delving into our comprehensive guide on these remarkable creatures.

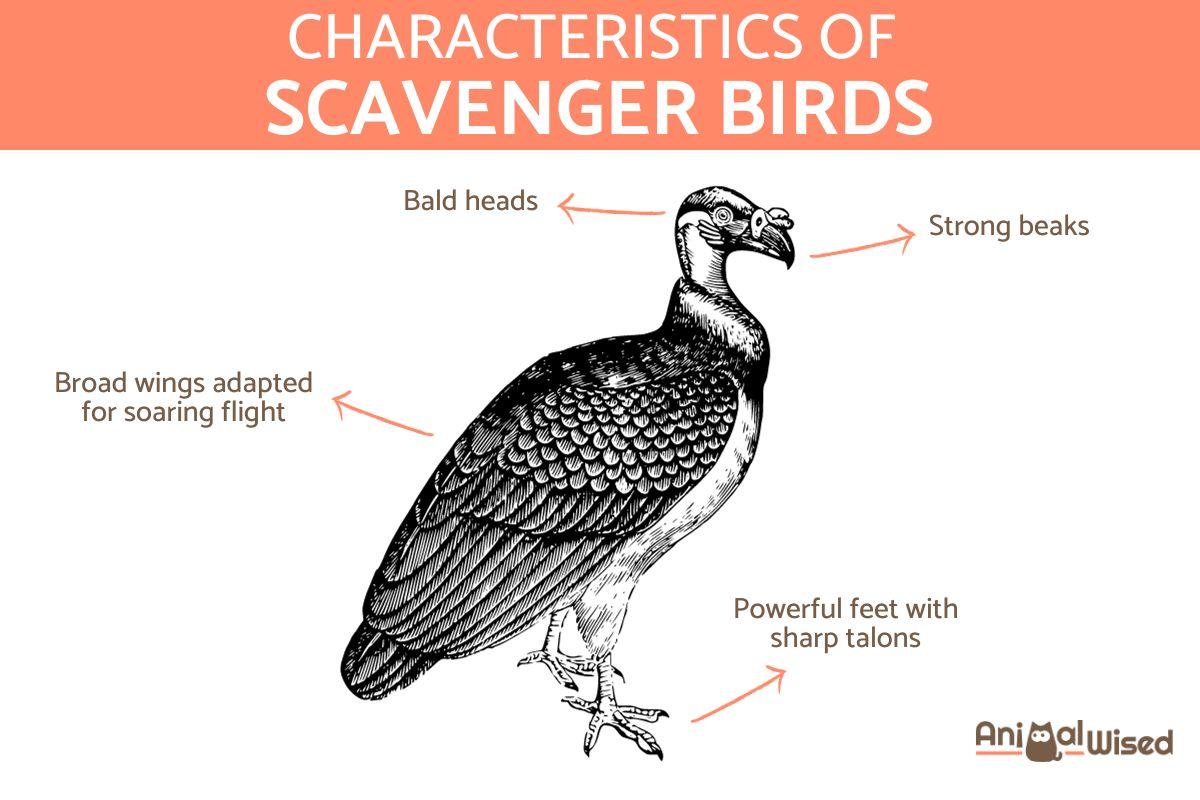
Characteristics of scavenger birds
Scavenger birds possess a set of characteristics that are well-suited to their scavenging lifestyle. These traits enable them to efficiently locate, consume, and derive sustenance from carrion. Here are some key characteristics of scavenger birds:
- Keen eyesight: scavenger birds typically have excellent eyesight, allowing them to spot carrion from great distances. This visual acuity is crucial for locating potential food sources.
- Strong beaks: many scavenger birds have powerful and robust beaks that are adapted for tearing into the tough flesh of carcasses. This feature is especially evident in vultures, which rely on their beaks to access and consume carrion.
- Bald heads: some scavenger birds, such as vultures, have bald or nearly bald heads. This adaptation helps prevent feathers from becoming soiled with blood and other fluids while feeding on carrion. It also minimizes the risk of bacterial growth.
- Specialized digestive systems: scavenger birds often have highly acidic stomachs and digestive enzymes that allow them to consume and digest decaying flesh. This adaptation helps neutralize the harmful bacteria present in carrion.
- Flight adaptations: many scavenger birds are adapted for soaring flight. Vultures, for example, are known for their impressive soaring abilities, allowing them to cover large distances in search of carrion.
- Intelligence: some scavenger birds, such as crows and ravens, are highly intelligent. Their cognitive abilities enable them to solve problems and adapt to a variety of environments. This intelligence is valuable in locating and accessing food, including carrion.
- Versatile diet: scavenger birds are opportunistic feeders and often have a versatile diet. While carrion is a primary food source, many scavenger birds can also consume a variety of other foods, including small animals, insects, fruits, and human food scraps.
- Social behavior: some scavenger birds exhibit social behavior, gathering in groups around carrion. Vultures, for example, may form large flocks at carcass sites. This behavior can provide safety in numbers and increase the efficiency of locating food.
Uncover the broader world of nature's cleanup team in our companion article on scavenger animals, with examples.

Types of scavenger birds
While scavenger birds don't have a specific taxonomic classification comparable to herbivorous birds, we can broadly categorize them based on their scavenging habits.
Two main types emerge from this distinction:
Specialized scavenger birds
These birds predominantly rely on consuming corpses or the remains of deceased animals as a significant part of their diet. Notable examples include vultures and condors, which have evolved specific adaptations like powerful beaks and keen senses to efficiently locate and feed on carrion.
Opportunistic scavenger birds
Opportunistic scavengers, on the other hand, do not solely depend on carrion but may consume it when the opportunity arises. Their diet is more diverse, encompassing live prey as well. Species like crows, ravens, eagles, and kites fall into this category. These birds exhibit adaptability, scavenging when other food sources are scarce or when carrion is readily available.
This classification sheds light on the range of scavenging behavior among birds, recognizing that some species have specialized and evolved to be highly efficient scavengers, while others incorporate scavenging into a broader and more varied feeding strategy.
Examples of scavenging birds
There is an important diversity of birds that eat dead animals which, as we already know, can be specialists or opportunists. Let's get to know some examples of scavenger birds:
Vultures
Vultures are the most specialized scavenger birds, belonging to the order Falconiformes. While there are taxonomic debates surrounding the group, they are generally classified into New World vultures and Old World vultures.
New World Vultures
New World vultures, found in the Americas, are slightly less specialized than their Old World counterparts. While their primary diet consists of carrion, they can also supplement their diet with live prey, such as small mammals and reptiles. Examples of New World Vultures include:
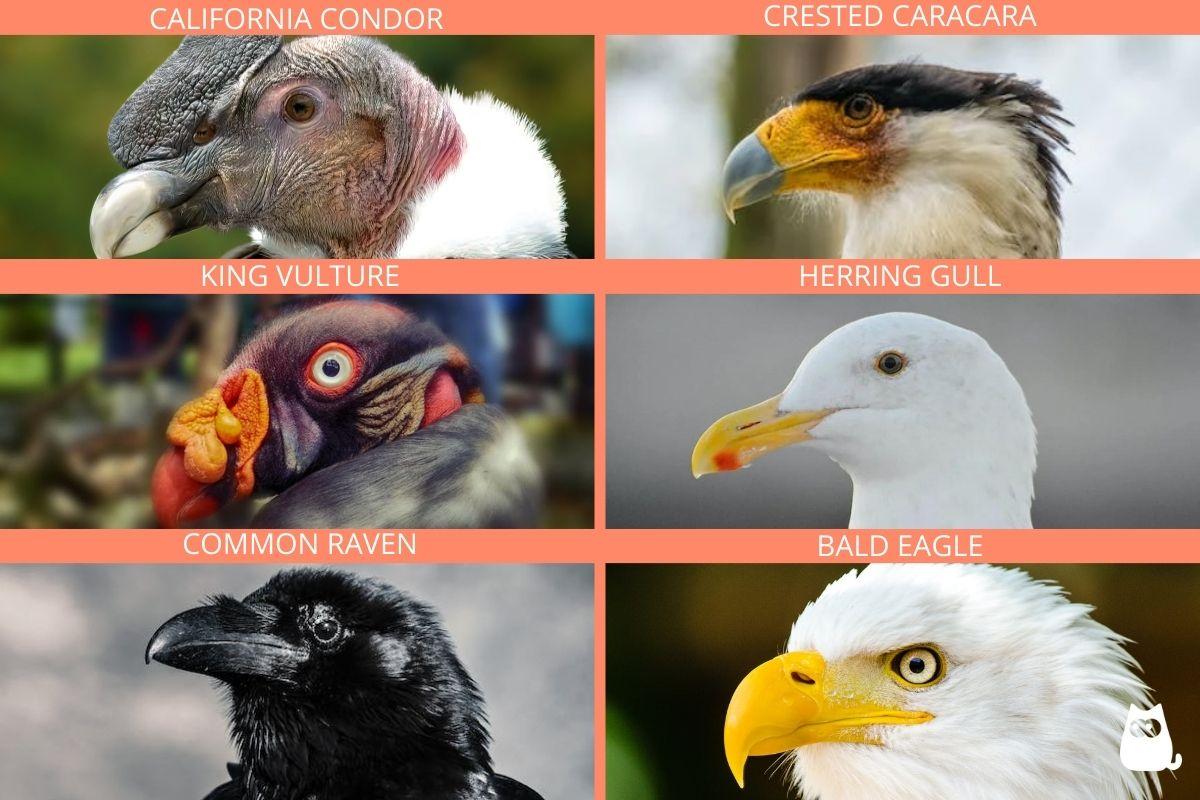
- California condor (Gymnogyps californianus): this critically endangered vulture prefers the remains of large prey, including cows, deer, horses, sheep, and coyotes. It initially opts for recently killed animals but resorts to those available when fresh carcasses are scarce.
- Turkey vulture (Cathartes aura): this widespread vulture is an opportunistic scavenger, consuming a wide range of carrion, from small rodents to large mammals. It is also known to feed on dead fish and occasionally fruits.
Old World Vultures
Old World vultures, inhabiting Africa, Europe, and Asia, are highly specialized scavengers. They have lost their hunting ability and rely solely on carrion for sustenance. Examples of Old World Vultures include:
- King vulture (Sarcoramphus papa): this massive vulture is a strict scavenger, known for its powerful beak that can pierce the skin of even the largest animals. It often displaces smaller vultures to steal their food.
- Indian white-backed vulture (Gyps bengalensis): this vulture species was once abundant across India but has declined drastically due to diclofenac poisoning. It is now critically endangered.
Crows
Crows, belonging to the Corvidae family, are highly intelligent birds known for their adaptability and opportunistic feeding habits. While they are primarily omnivores, consuming a wide variety of food items, they exhibit a strong inclination towards scavenging. Some popular examples of crows include:
- Common raven (Corvus corax): this large, black crow is a widespread scavenger, consuming a variety of carrion, including small mammals, birds, and reptiles. It is also known to scavenge on roadkill and human food scraps.
- Carrion crow (Corvus corone): this medium-sized crow is found across Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. It is a versatile scavenger, consuming a wide range of carrion, including small mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish.
- American crow (Corvus brachyrhynchos): this common crow is found across North America. It is a highly opportunistic scavenger, consuming a variety of carrion, including small mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish. It is also known to scavenge on roadkill and human food scraps.
If the scavenger birds' tales left you hungry for more avian adventures, soar into the intriguing universe of crow communication.
Caracaras
Caracaras are a group of birds that belong to the falcon family (Falconidae). Unlike their more agile and predatory falcon cousins, caracaras exhibit a more laid-back approach to life, often opting for scavenging as their primary means of sustenance. They are found primarily in the Americas, inhabiting a diverse range of habitats, from open grasslands to dense forests. Examples of Caracaras include:
- Crested caracara (Caracara cheriway): this widespread caracara is found across South America, inhabiting grasslands, forests, and open country. It is known for its distinctive crest of feathers and its preference for carrion.
- Common caracara (Caracara plancus): this adaptable caracara is found across Central and South America, inhabiting a variety of habitats, including grasslands, forests, and mountains. It is a versatile scavenger, consuming a wide range of food items.
- Caracara dawning (Caracara lunatus): this forest-dwelling caracara is found primarily in the Amazon rainforest. It is a less common caracara, known for its shy and elusive behavior.
Gulls
Gulls, belonging to the Laridae family, are a diverse and widespread group of birds found along coastlines, inland waterways, and even urban environments. They are characterized by their webbed feet, strong beaks, and ability to adapt to a variety of feeding strategies. While gulls are primarily omnivores, consuming a wide range of food items, they are also adept scavengers. Some examples of scavenger gulls include:
- Herring gull (Larus argentatus): this large and common gull is found along coastlines worldwide. It is an opportunistic scavenger, consuming a wide range of carrion, including fish, birds, and small mammals.
- Lesser black-backed gull (Larus fuscus): this mid-sized gull is found along coastlines and waterways in Europe, Asia, and parts of North America. It is a skilled scavenger, often following fishing vessels to scavenge for discarded fish.
- Glaucous gull (Larus hyperboreus): this large, white gull is found in Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. It is a powerful scavenger, capable of consuming carrion as large as small seals and walruses.
Eagles
Eagles, majestic birds of prey belonging to the Accipitridae family, are renowned for their soaring flight, powerful talons, and sharp beaks. While they are often associated with hunting and predation, eagles exhibit a remarkable adaptability and opportunistic feeding habits, making them skilled scavengers as well.
- Bald eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus): this iconic American eagle is found across North America, inhabiting a variety of habitats, including forests, lakes, and coastlines. It is an opportunistic scavenger, consuming a wide range of carrion, including fish, birds, and small mammals.
- Golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos): this large and powerful eagle is found across North America, Eurasia, and parts of Africa. It is a versatile scavenger, consuming a wide range of carrion, from small mammals to large ungulates.
- White-tailed eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla): this Eurasian eagle is found across Europe, Asia, and parts of North Africa. It is a skilled scavenger, often following human activities to locate food sources.
Do not miss the following article on how do eagles hunt.

If you want to read similar articles to Scavenger Birds - Types and Characteristics, we recommend you visit our Facts about the animal kingdom category.
Animal Diversity Web (2020). Available at: https://animaldiversity.org/
Hickman, C.; Roberts, L.; Parson A. (2000). Comprehensive principles of zoology. McGraw Hill Inter-American: Spain.
Ospina S., Pedro, Ramírez V., Mercy, & Maturrano H., Lenin. (2021). Vultures, scavenger birds of the Old World and New World. Journal of Veterinary Research of Peru , 32 (5), e21337. Epub October 27, 2021. https://dx.doi.org/10.15381/rivep.v32i5.21337