Types of Lupus in Dogs - Symptoms and Treatment



See files for Dogs
Lupus in dogs is an autoimmune disease which can present in two main forms. The type of lupus in dogs depends on whether it is limited to the skin or if it has spread throughout the organism. It is important to know the nature of each canine lupus case as this will determine the course of treatment required and, vitally, the prognosis for the individual dog.
In this AnimalWised article, we will learn how to identify the types of lupus in dogs. In doing so, we will be able to determine which type is affecting your dog. After this has been determined, we can show you what treatment options are available and how you will need to act to manage the condition.
What is lupus?
Lupus is an autoimmune disease. This means it is a pathology which attacks the organism on a cellular level and affects its ability to defend itself against infections. More specifically, it is a disease which affects the basal cell layer of the skin or in certain organs. It is believed there may be some predisposing factors such as exposure to ultraviolet rays, administration of modified live virus vaccinations or the individual's genetic history. There is a common misconception among dog guardians that lupus is a form of cancer, but this is not the case.
When we want to look at the different types of lupus in dogs, we can see there are two main manifestations. They are systemic lupus erythematosus and discoid lupus erythematosus. The former is a multisystem autoimmune disorder, the latter a more localized condition which is limited to the skin and is considered milder and more benign.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
In the systemic form of lupus in dogs, we see a variety of symptoms. The exact manifestation of these symptoms will depend on the different organs affected, the most common being the skin, kidneys and heart. It can also affect joint tissue. Joint pain, episodic fever, kidney failure or anemia can occur. If the mouth is affected, then stomatitis may occur.
Additionally, lesions appear on the skin due to ulceration. The face is usually the place with the greatest concentration of lesions, especially on the nose which can lose its natural texture. The legs can also become ulcerated, with the paw pads having the potential to thicken and even fall off due to contact with the ground. The are surrounding the dog's nails can also be infected and lead to the nails coming out of their beds. Skin problems can progress to crusting and alopecia. The first symptom may be a limp or uneven gait.
Discoid lupus erythematosus
Discoid lupus erythematosus is a relatively common immune disease which results in limited concentration of lesions on the face and ears. In some dogs, however, it is possible to see skin problems on the genitals or paw pads. The first signs of lupus of this type are small colorless lesions which may redden over time. Given further time, they can ulcerate and scab over.
Depending on the individual case, there will also be pain and itching. We may notice that sunlight worsens the symptoms. It appears there are certain breeds with a greater predisposition to this problem. These breeds include the Border Collie, the German Shepherd and the Siberian Husky.
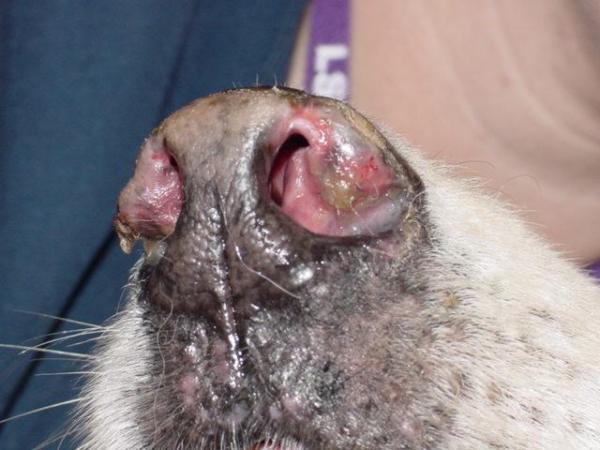
Diagnosis of lupus in dogs
At first, it may be difficult to realize our dog is suffering from systemic lupus. The reason for this is, as we have seen from the symptoms of lupus in dogs, the symptomatology can be varied and is similar to other pathologies. To accurately diagnose lupus in dogs, we have to rule out any other causes. To do this, the veterinarian will look closely at the clinical history of the dog as well as giving them a physical examination, but this is not all.
Several tests are usually required to reach a confident lupus diagnosis. It will be essential to perform urinalysis and a blood test. However, for a definitive diagnosis, it will be necessary to perform an antibody test and biopsy. The latter is one of the reasons many guardians believe lupus is a form of skin cancer.
With cases of discoid lupus erythematosus, its identification is more simple due to the appearance and location of the lesions. If the dog does not present any further symptoms, it is possible for a qualified vet to make a direct diagnosis.
Treatment of lupus in dogs
Lupus in dogs is a pathology with specific treatment, but it will depend on the type and acuteness of the condition. In the case of discoid lupus erythematosus, oral and topical medication might be prescribed. These will be based on corticosteroids and antibiotics, if necessary. Some studies suggest vitamin E supplements may be useful. For systemic lupus erythematosus, immunosuppressants must be used to stop the organisms attack against itself. Since the disease affects certain organs, the effects of lowered organ functionality will also need to be treated.
In general it is necessary to avoid exposure to sunlight or apply the use of skin protection. UV rays can aggravate the condition and can increase discomfort. It can also make them more susceptible to other diseases such as skin cancer.
Systemic lupus in dogs is not curable, but it is manageable. Obtaining a prompt diagnosis and following the correct veterinary treatment can help reduce the chances of remission in a dog.

Is lupus in dogs contagious?
After discussing the symptoms and treatment of lupus in dogs, it is natural to ask if it is contagious. Fortunately, this is not a contagious condition. Instead, it is an immune system problem which affects the organism's own cells. This defect is not contagious and it cannot be transferred from one dog to another. Neither is lupus in dogs zoonotic. This means it cannot be passed on from canine to human. It is not necessary to establish a quarantine or other control measures, but it will be important to keep the dog from scratching at any lesions.
Life expectancy of dogs with lupus
As we can see, there is treatment for lupus in dogs, but it will depend on the type and whether it is managed correctly. With systemic lupus, the disease can affect specific organs. If their functionality is lowered, it can seriously damage the overall health of the dog. The clinical picture can be particularly delicate when the kidneys are involved. Kidney failure is irreversible and it may cause a wide range of health problems.
On the other hand, discoid lupus can usually be more manageable and can go into remission more easily. For systemic lupus, the compromised immune system makes the dog more vulnerable to other infections and problems. While the lupus itself may not affect their life expectancy, the secondary conditions might. It is imperative we consult a veterinarian to ensure the best course of treatment is provided. Monitoring the condition and providing hygienic living conditions are the best ways to ensure longevity. Also be careful when out on walks or interacting with other dogs.
This article is purely informative. AnimalWised does not have the authority to prescribe any veterinary treatment or create a diagnosis. We invite you to take your pet to the veterinarian if they are suffering from any condition or pain.
If you want to read similar articles to Types of Lupus in Dogs - Symptoms and Treatment, we recommend you visit our Other health problems category.








